What Is Tissue Transglutaminase IgA Test?
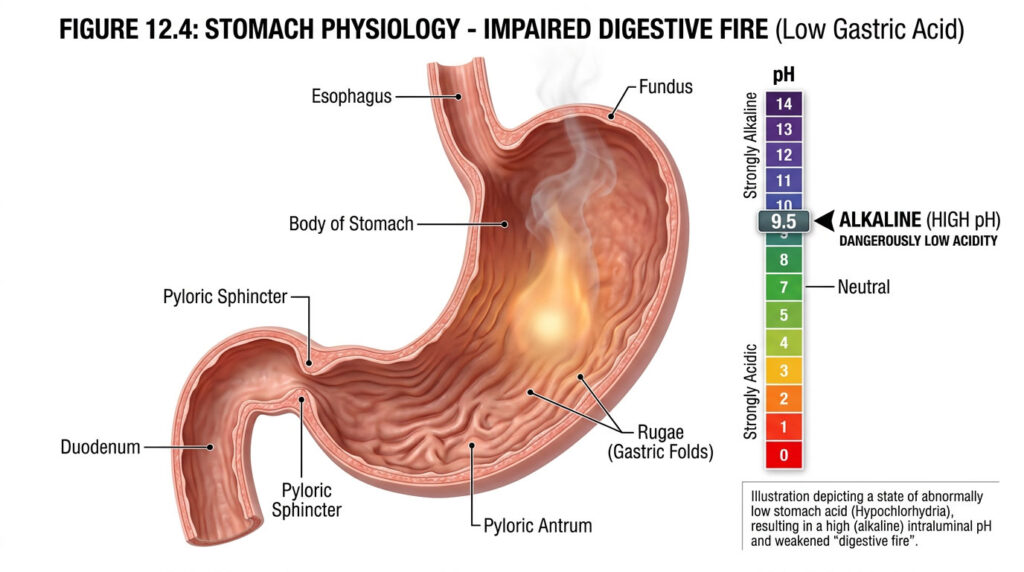
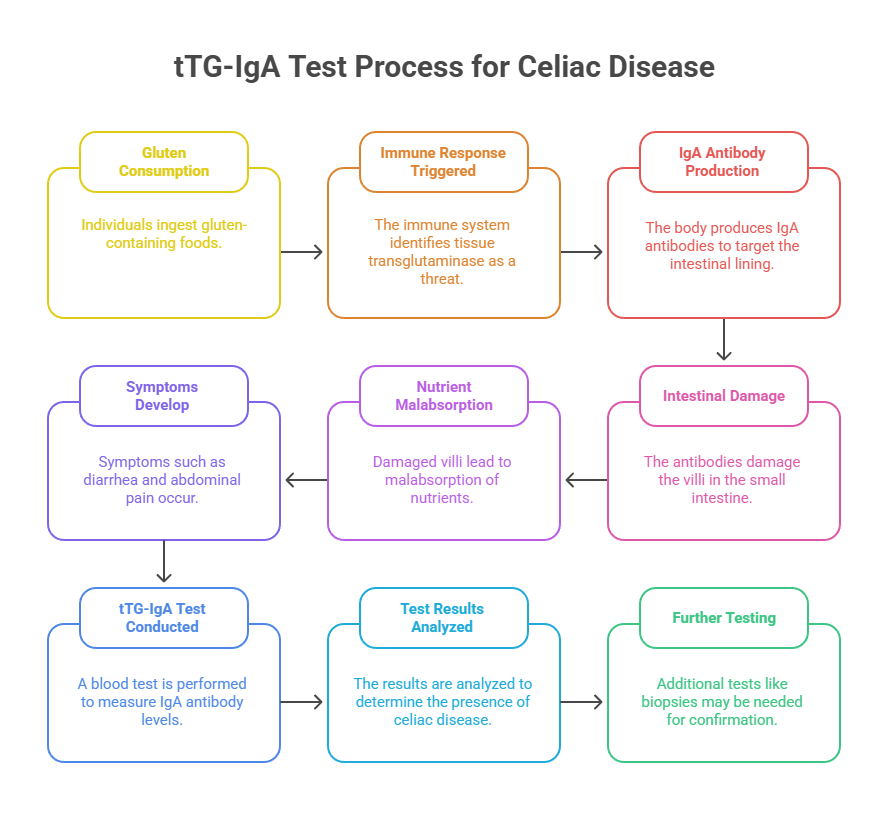
The tTG test, also known as the tissue transglutaminase test, is a blood test used to diagnose celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder characterized by an adverse reaction to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. The test measures the number of antibodies called anti-tissue transglutaminase IgA in the blood.
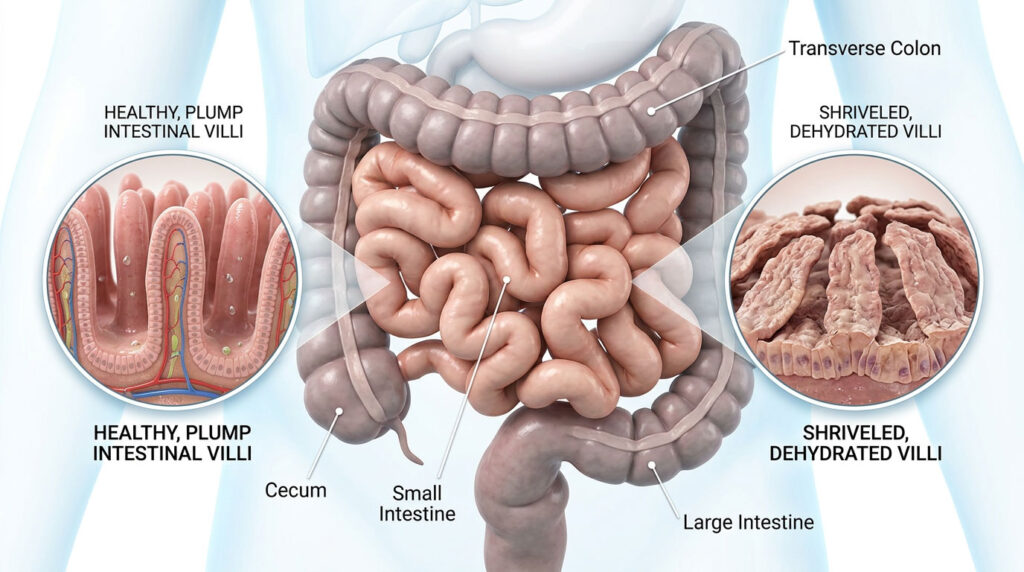
Tissue transglutaminase is an enzyme that plays a role in the breakdown of gluten in the small intestine. In people with celiac disease, the immune system mistakenly identifies tissue transglutaminase as a foreign invader and produces antibodies against it. The antibodies then attack the intestinal lining, causing inflammation and damage to the villi, small finger-like projections that absorb nutrients from food.
About tTG-IgA Test
Why Do I Need tTG Blood Test?
You may need the iITG-IgA test because of the following reasons.
- Suspected celiac disease: Your doctor may order the tTG-IgA test to help confirm the diagnosis if you exhibit symptoms that point to celiac disease, such as gastrointestinal symptoms like abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, bloating, and gas or non-gastrointestinal symptoms like fatigue, anemia, weight loss, skin rash, joint pain, and depression.
- Family history of celiac disease: Because the condition can run in families, your doctor could advise getting tested for it if you have a family member who suffers from it.
- Screening for celiac disease: Even if you don’t have any symptoms, your doctor may advise you to get screened for celiac disease if you have specific medical conditions linked to an increased risk of the disease, such as type 1 diabetes, Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, autoimmune thyroid disease, or selective immunoglobulin A deficiency.
- Treatment tracking: If you have celiac disease and are on a gluten-free diet, your doctor may ask for the tTG test to track your development and make sure you stay on the diet.
- Testing for gluten sensitivity: Although they may not have celiac disease, some people may occasionally have symptoms that are comparable to it. In these circumstances, your doctor could request the tTG-IgA test to determine gluten sensitivity.
Several tests can be used to identify celiac illness; this tTG-IgA testing is the simplest. A combination of blood testing, genetic tests, and a small intestine biopsy is typically necessary for a conclusive diagnosis.
How To Prepare For tTG Antibody Test?
- Talk to your doctor: Your doctor may give you specific instructions on preparing for the test based on your medical history and current health status.
- Do not stop eating gluten: If you suspect you have celiac disease or have been diagnosed with it, do not stop eating gluten before the test. This is because the tTG testing is designed to detect the presence of antibodies produced in response to gluten.
- Follow your regular medication routine: If you take any medications or supplements, continue taking them as usual unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
- Fast, if necessary: Depending on the specific test and the lab that performs it, you may need to fast for a certain amount before the blood draw. Your doctor will let you know if this is necessary.
- Inform the lab if you have bleeding disorders or are taking blood thinners: In some cases, bleeding can occur after a blood draw, which can be dangerous for people with bleeding disorders or those taking blood-thinning medications. Inform the lab if you have bleeding disorders or are taking blood thinners.
- Wear comfortable clothing: Choose loose-fitting clothing with sleeves that can easily be rolled up, as the blood will be drawn from your arm.
What Happens During Tissue Transglutaminase Antibody Testing?
Are you visiting your nearest diagnostic center to get an antibody test? If yes, your healthcare professional will take the following steps to draw the blood sample:
- Your healthcare provider will wrap a thin pipe around your arm and cleanse the target area with rubbing alcohol.
- The expert will check for the vein in your arm and ask you to clench your fists tightly.
- Your healthcare provider will draw a blood sample from your vein using a syringe and collect it in a vial/test tube, removing the injection from your skin.
- They will seal the target area with a bandage to avoid bleeding and send your blood sample to the laboratory for testing.
Finding tTG-IgA Test
Should you call for the tTG Test at home or get it done at your nearest clinic? Read more to find out what suits your comfort.
Can I Take tTG Antibody Test At Home?
The tTG-IgA test can’t be performed at home, A standard tTG blood test requires an experienced healthcare professional to draw a blood sample, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
While home test kits are available for some medical conditions, the tTG-IgA test is not one of them. It is vital to have the test done in a clinical setting, where a trained healthcare professional can ensure the accuracy of the test and provide appropriate medical guidance and follow-up care.
How Much Does tTG-IgA Test Cost?
The average tTG-IgA test price varies depending on various factors, such as where you live, the healthcare provider or laboratory that performs the test, and whether or not you have health insurance coverage. You can check the tTG IgA cost on our website. We offer this test at INR 1109. Our prices are lower than the average test prices without compromising on quality.
Test Results Interpretation
You received your tTG test results but still need help determining if you have antibodies in the normal range. Read this section to understand how to go about your antibody diagnoses with your healthcare professional.
What Do tTG-IgA Test Results Mean?
If you have taken the tTG-IgA test, here’s what your tTG antibody test results may mean:
- Negative result: A negative result means that no tTG-IgA antibodies were detected in your blood sample. It is generally considered a normal result and suggests that you do not have celiac disease or are not actively consuming gluten.
However, it’s important to note that a negative result does not entirely rule out the possibility of celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, especially if you have symptoms or a family history of the condition.
- Positive result: A positive result means that tTG-IgA antibodies were detected in your blood sample. It indicates that your body is immune to gluten and may suggest that you have celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. Further evaluation and testing, such as a small intestine biopsy, may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
- Borderline result: A borderline or weakly positive result means that tTG-IgA antibodies were detected in your blood sample. However, the levels were not high enough to definitively diagnose celiac disease or gluten sensitivity. Your healthcare provider may recommend additional testing or a gluten-free trial to evaluate your condition further.
What Is tTG IgA Test Normal Range?
Tissue Transglutaminase IgA Normal Range | Interpretation |
Less than 20 IU/mL | Negative |
20 IU/mL or greater | Positive |
The normal range for tTG-IgA can vary slightly depending on the laboratory that performs the test. In general, the tT-IgA test normal range is less than 20 U/mL.
If your test results fall within this range, it suggests that no tTG-IgA antibodies were detected in your blood sample, which is considered a normal result. However, it’s important to note that a normal result does not entirely rule out the possibility of celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, especially if you have symptoms or a family history of the condition.
What Medical Conditions Can Cause High tTG Level?
If you have a high tTG level, it could be indicative of a few different medical conditions. Here are some possibilities:
- Celiac disease: It’s an autoimmune disorder where the body attacks the lining of the small intestine in response to gluten consumption. A high tTG level is a standard marker of celiac disease.
- Dermatitis herpetiformis: This is a skin condition that’s closely linked to celiac disease. Dermatitis herpetiformis patients may have elevated tTG levels.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Conditions such as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can cause digestive tract inflammation, which can result in increased tTG levels.
- Type 1 diabetes: Those who have Type 1 diabetes may also have celiac disease and a high tTG level.
What Medical Conditions Can Cause Low tTG Level?
You might not have celiac disease or other gluten-related illnesses if your tTG level is low. A low tTG level, nevertheless, could be brought on by additional health issues. Here are some potential examples:
- IgA deficiency:Some people’s bodies do not manufacture enough IgA antibodies, which might result in a false negative tTG test result.
- Gluten sensitivity:Although not as severe as celiac disease, some persons may have diarrhea or abdominal pain after ingesting gluten. However, these individuals may not have a high enough tTG level to be diagnosed with celiac disease.
- Intestinal damage from non-gluten sources:Other conditions, such as infections or medications, can cause damage to the intestinal lining that may lead to a low tTG level.
- Early stages of celiac disease: In some cases, a person with celiac disease may have a low tTG level early on in the disease process before it progresses to the point where tTG levels are elevated.
Why Choose HealthcareOnTime
Convenience at Your Doorstep
Ever wished for healthcare that comes to you? HealthcareOnTime makes it a reality with doorstep lab testing, cutting out clinic hassles. No more queues or travel stress. Experience at-home sample collection, prioritizing health without time constraints. —your path to health, now just a doorstep away!
Affordable Testing with Thyrocare Partnership
Experience cost-effective lab testing at-home with HealthcareOnTime’s exclusive partnership with Thyrocare. Benefit from competitive prices while ensuring precise results. Our collaboration with Thyrocare Technologies Limited guarantees affordability without compromising on the accuracy and reliability of your lab test.
Comprehensive Health Screening
At HealthcareOnTime, we’ve got your back with our comprehensive health checkup packages! Take charge of your well-being by booking online. These packages empower you to stay ahead, catching potential issues early for timely management. It’s like having a health ally, and making informed decisions for a healthier, happier life.
Disclaimer: Although we have endeavored to provide accurate information on this page, we strongly recommend that you seek advice from your doctor before relying on any of the test ranges or lab-test recommendations mentioned herein.
Ref Links:
- https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=167&contentid=antitissue_transglutaminase_antibody
- https://www.lybrate.com/lab-test/anti-ttg-iga
- https://www.practo.com/tests/tissue-transglutaminase-antibodies-iga-elisa-blood/p
More Related Tests
Why To Book with HealthCareOnTime
17 Crores+ Samples Processed
World Class Technology Labs

25+ Years of Trust & Experience

Free Home Collection
FAQs Around tTG-IgA Test (Tissue Transglutaminase IgA)
What is the normal range for celiac?
The normal range to detect celiac disease is 20 U/mL.
What is the most accurate test for celiac disease?
The most accurate test involves a combination of blood test for celiac disease and an intestinal biopsy. Blood tests measure the levels of specific antibodies (tissue transglutaminase (tTG) and deamidated gliadin peptide (DGP) & their presence at high levels, suggest that you might have celiac disease.
What iga level indicates celiac?
Celiac disease gets indicated if your IgA level is beyond 20 U/mL.
What does a positive tTG igg mean?
A positive tTG IgG test result usually indicates the presence of antibodies against tissue transglutaminase (tTG) in the blood. However, a positive tTG IgG result alone is insufficient for diagnosis, & further evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary to confirm the disease.
What does a negative tTG igg mean?
A negative tTG IgG test result means medical experts couldn’t detect antibodies against tissue transglutaminase (tTG). However, a negative tTG IgG result doesn’t rule out the presence of the disease. Further, evaluation by a healthcare professional may be needed to confirm or rule out a diagnosis.
Can a CBC test detect celiac disease?
A CBC Test alone cannot detect celiac disease. However, it can identify anemia or other blood-related conditions associated with celiac disease. The diagnosis usually involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, and intestinal biopsy.