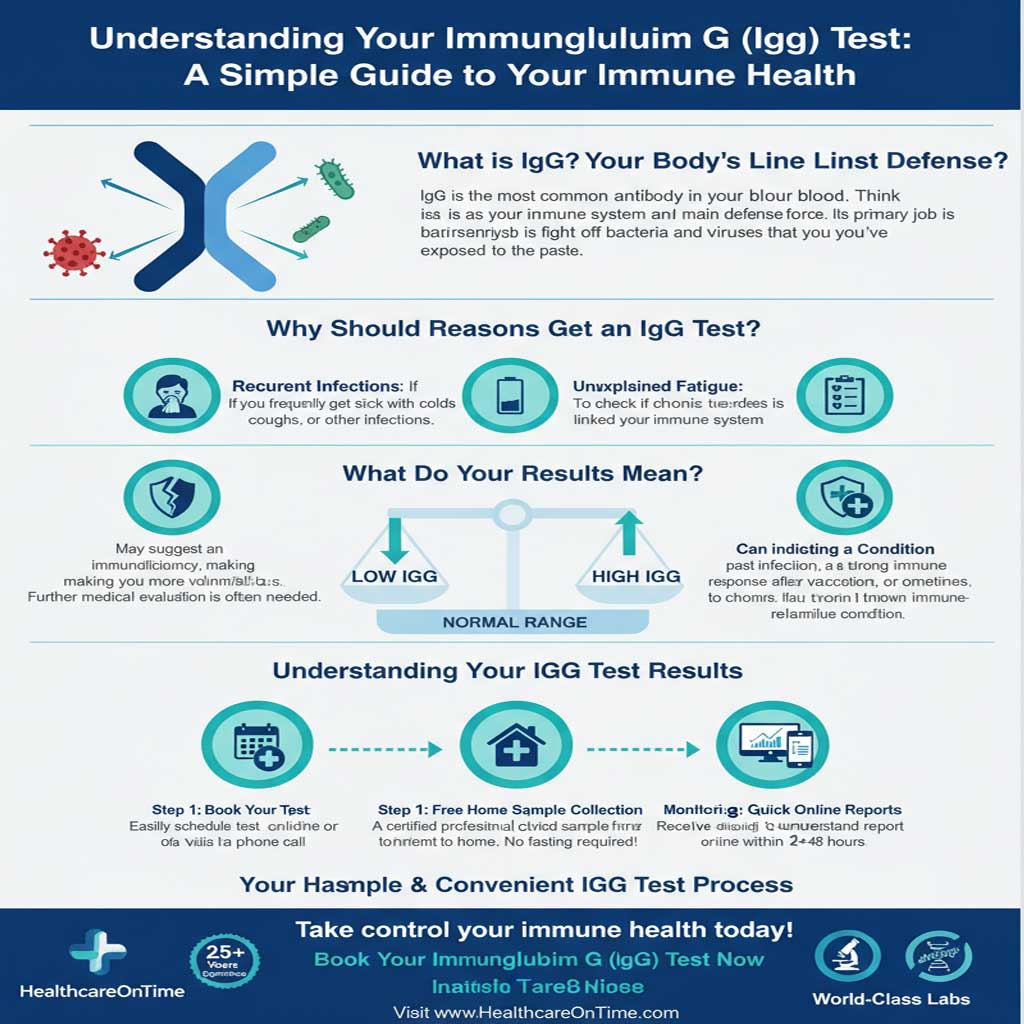
What Is Immunoglobulin G Test
The Immunoglobulin G or IGG test is one of the standard blood tests done to measure the amount of Immunoglobulin G antibodies present in your bloodstream. It is a laboratory procedure that assists in determining the blood levels of immunoglobulins A, G, and M. These immunoglobulins are antibodies produced by the human immune system to combat infection.
About IgG Test
Learn everything about IgG Blood Testing before you book lab test online. Understand the why, how, and what of this test.
Why Do I Need Immunoglobulin G Test?
Here are a few reasons why you need an IgG antibody test:
- Helps you determine whether or not you’re exposed to any disease.
- Aids in assessing immunity levels following sickness recovery or immunisation.
- Useful in cases of persistent inflammation.
- Assists you in cases of recurrent infections if IgG antibodies are the source of the infection.
How To Prepare For IgG Blood Test?
To prepare for IgG Test, follow these steps: Consult your healthcare provider, inform them about medications, avoid intense exercise, follow fasting instructions if given, and provide accurate medical history.
What Happens During IgG Blood Testing?
A IgG Blood test only takes a few minutes.
- As per the scheduled time of the blood test, a lab technician who usually takes blood samples will arrive.
- A thin needle will be used to draw blood from your arm’s vein.
- The needle might cause a mild pinch and some discomfort.
- The lab technician then fills a collection tube with blood and then removes the needle from the skin.
- They place a small bandage on the arm.
Finding IgG Test
Should you book blood test online to check your IgG levels or go to the nearest clinic and get it done by a medical professional? Let’s Find Out
Can I Take IgG Lab Test At Home?
Yes, the IgG blood testing can be taken at home. HealthcareOnTime’s at-home lab testing service in association with Thyrocare, provides a convenient and efficient way to get important medical tests done from the comfort of your place, without the need for a doctor’s visit or a trip to a lab. It is always preferable to consult with a healthcare provider about any concerns regarding your test results.
How Much Does IgG Test Cost?
The IgG test price varies depending on various factors, such as where you live, the healthcare provider or a laboratory that performs the test, and whether or not you have health insurance coverage. You can check the IgG blood test price on our website. We offer this test at INR 729. Our prices are lower than the average test prices without compromising on quality.
Test Result Interpretation
You received your IgG blood test results but still need help determining if they fall under the normal range. Read this section to understand whether your results are within the Immunoglobulin G normal range or not.
What Does Immunoglobulin G Test Results Mean?
The IgG test results interpretation is often categorised as high or low IgG levels. High IgG levels can result from autoimmune diseases, including cirrhosis, infections in the body, or reactivity to specific chemicals. Low levels of IgG point to protein loss from the body, which diabetes, a sickness, burns, or other trauma may bring on.
What Is Immunoglobulin G Test Normal Range?
The IgG normal range for different age groups is:
Age Group (years) | Normal IgG Levels by Age |
0-1 | 231-1411 mg/dL |
1-3 | 453-916 mg/dL |
4-6 | 504-1464 mg/dL |
7-9 | 572-1474 mg/dL |
10-11 | 698-1560 mg/dL |
12-13 | 759-1549 mg/dL |
14-15 | 716-1711 mg/dL |
16-19 | 549-1584 mg/dL |
Above 19 | 700-1600 mg/dL |
What Medical Conditions Can Cause High Immunoglobulin G Level?
The medical conditions responsible for causing high Immunoglobulin G levels in your body are:
- Hepatitis – An inflammatory condition of the liver caused by hepatitis virus.
- Chronic infection
- Autoimmune disease – Autoimmune hepatitis is a condition wherein your body’s immune system attacks your liver.
- Liver Cirrhosis – A result of chronic alcoholism, cirrhosis is often associated with symptoms, such as degeneration of liver cells, fibrous thickening of cells, inflammation, etc.
- Cancers like lymphoma, multiple myeloma, etc.
What Medical Conditions Can Cause Low Immunoglobulin G Level?
The medical conditions responsible for causing low Immunoglobulin G levels in your body:
- Protein-reducing conditions in the body like serious burns, kidney disease, and malnutrition.
- Conditions damaging your body’s ability to produce immunoglobulins like kidney failure and diabetes.
- Genetic conditions like CVID or Common Variable Immunodeficiency Disorder, which leads you to have repeated infections due to low levels of infection-fighting protein levels.
Why Choose HealthcareOnTime?
Convenience at Your Doorstep
Ever wished for healthcare that comes to you? HealthcareOnTime makes it a reality with doorstep lab testing, cutting out clinic hassles. No more queues or travel stress. Experience at-home sample collection, prioritizing health without time constraints. —your path to health, now just a doorstep away!
Affordable Testing with Thyrocare Partnership
Experience cost-effective lab testing at-home with HealthcareOnTime’s exclusive partnership with Thyrocare. Benefit from competitive prices while ensuring precise results. Our collaboration with Thyrocare Technologies Limited guarantees affordability without compromising on the accuracy and reliability of your lab test.
Comprehensive Health Screening
At HealthcareOnTime, we’ve got your back with our comprehensive health checkup packages! Take charge of your well-being by booking online. These packages empower you to stay ahead, catching potential issues early for timely management. It’s like having a health ally, and making informed decisions for a healthier, happier life.
Sources
Ref Links:
- https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/immunoglobulins-blood-test/
- https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/immunoglobulin-test
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/igg-deficiencies
More Related Tests
Why To Book with HealthCareOnTime
17 Crores+ Samples Processed
World Class Technology Labs

25+ Years of Trust & Experience

Free Home Collection
FAQs Around Immunoglobulin g (IgG) Test
Is high IgG good or bad?
High IgG levels can be both good and bad, depending on the context. In general, elevated IgG indicates a robust immune response, which is beneficial for fighting infections and providing immunity. However, persistently high IgG levels may also suggest certain autoimmune or inflammatory conditions.
Is low IgG serious?
Yes, low IgG levels can be serious. IgG is a crucial antibody for immune function and defense against infections. Low IgG levels may lead to an increased susceptibility to infections, particularly bacterial and viral ones. It can also indicate underlying immunodeficiency disorders.
What is IgG deficiency disease?
IgG deficiency disease, also known as Selective IgG Deficiency, is a medical condition characterized by lower than normal levels of Immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies in the blood. This primary immunodeficiency disorder can lead to an increased risk of infections, especially respiratory and gastrointestinal infections.










