Immunoglobulin E (IgE) and Serum Immunoglobulin E: Understanding its Role in the Immune System
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a type of antibody that plays a crucial role in the immune system. It is responsible for the allergic response and the defense against parasites. Serum Immunoglobulin E is the measure of the amount of IgE in the bloodstream. In this blog, we will discuss the functions of IgE, its role in the immune system, how Serum Immunoglobulin E is measured, and what high and low levels of Serum Immunoglobulin E mean. We will also answer some frequently asked questions about Serum Immunoglobulin E.
What is the function of IgE?
Overview of IgE function in the immune system
IgE is a type of antibody that is produced by plasma cells in response to the presence of allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, and animal dander. When IgE binds to an allergen, it triggers the release of chemicals, such as histamine, from mast cells and basophils, causing an allergic reaction.
Apart from its role in allergies, IgE also plays a crucial role in the immune system’s response to parasites, such as helminths. It triggers the release of chemicals that cause the expulsion of parasites from the body.
Importance of IgE in the response to allergens
IgE is the key player in the allergic response. It is responsible for the symptoms associated with allergies, such as sneezing, itching, and swelling. When an allergen enters the body, it triggers the production of IgE, which binds to the allergen, causing the release of histamine and other chemicals that cause inflammation and allergic symptoms.
Role of IgE in allergic reactions
Allergic reactions occur when the body’s immune system overreacts to harmless substances, such as pollen or pet dander. IgE is produced in response to these substances and binds to mast cells and basophils, which are found in tissues throughout the body. When IgE binds to these cells, it triggers the release of chemicals that cause an allergic reaction, such as swelling, redness, and itching.
How is Serum Immunoglobulin E Measured?
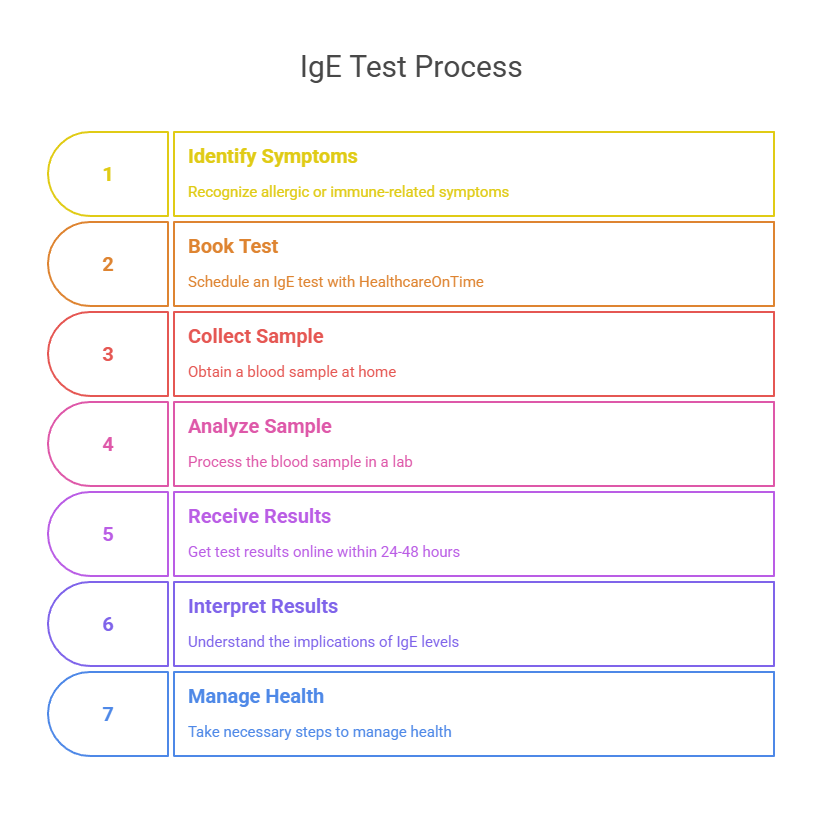
Overview of the Serum Immunoglobulin E test
Serum Immunoglobulin E is measured using a blood test. The test measures the amount of IgE in the bloodstream. The normal range of Serum Immunoglobulin E levels varies from person to person and depends on various factors, such as age, gender, and overall health.
When is the test used?
The Serum Immunoglobulin E test is usually performed to diagnose allergies and asthma. High levels of Serum Immunoglobulin E are often seen in people with allergies and asthma. The test is also used to monitor the effectiveness of treatment for allergies and asthma.
Preparation for the test and what to expect
No special preparation is required for the Serum Immunoglobulin E test. The test is performed by drawing blood from a vein in the arm. The procedure is usually quick and painless, and there are no significant risks or side effects associated with the test.
What Does High Serum Immunoglobulin E Mean?
High serum immunoglobulin E levels indicate that the body is producing an excessive amount of IgE antibodies. This can be a sign of allergies, asthma, or other immune system disorders. Some of the common causes of high serum IgE levels are:
- Allergies: Allergic reactions occur when the body produces an excessive amount of IgE in response to allergens such as pollen, dust, or pet dander.
- Asthma: Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease that is often associated with high levels of serum IgE.
- Parasitic infections: Certain types of parasitic infections can stimulate the body to produce large amounts of IgE.
- Autoimmune diseases: Autoimmune diseases such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can cause high levels of serum IgE.
Treatment for high serum IgE levels depends on the underlying cause. For allergies and asthma, medications such as antihistamines or corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce the production of IgE antibodies. Immunotherapy, which involves exposing the patient to small doses of the allergen over time, can also help reduce the body’s sensitivity to the allergen.
What Does Low Serum Immunoglobulin E Mean?
Low serum immunoglobulin E levels can indicate an immune deficiency. A low level of IgE in the blood can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Primary immunodeficiencies: Some individuals are born with an immune system that doesn’t function properly, which can result in low levels of IgE.
- Secondary immunodeficiencies: Certain medications, diseases, or infections can weaken the immune system and lead to low levels of IgE.
- Aging: As individuals age, their immune system can become less efficient, resulting in lower levels of IgE.
Treatment for low serum IgE levels depends on the underlying cause. For primary immunodeficiencies, treatments may include bone marrow or stem cell transplants. For secondary immunodeficiencies, treating the underlying condition can help improve IgE levels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, serum immunoglobulin E levels play an important role in the immune system’s response to allergens and infections. High levels of serum IgE can be a sign of allergies, asthma, or other immune system disorders, while low levels can indicate an immune deficiency. Understanding your serum IgE levels and working with your healthcare provider to address any issues can help support a healthy immune system and overall well-being.
More Related Tests
Why To Book with HealthCareOnTime
17 Crores+ Samples Processed
World Class Technology Labs

25+ Years of Trust & Experience

Free Home Collection
FAQs Around IMMUNOGLOBULIN E (IGE) Test
Can you have high Serum Immunoglobulin E levels without having allergies?
Yes, high serum immunoglobulin E levels can be caused by factors other than allergies, such as asthma, parasitic infections, or autoimmune diseases.
Is there a way to lower Serum Immunoglobulin E levels naturally?
There is no proven natural way to lower serum immunoglobulin E levels. However, some studies suggest that a healthy diet and lifestyle, including regular exercise and stress management, may help support a healthy immune system.
What are the risks of having low Serum Immunoglobulin E levels?
Low serum immunoglobulin E levels can increase the risk of developing infections, particularly those caused by parasites. Individuals with low IgE levels may also be more susceptible to certain autoimmune diseases.
Can Serum Immunoglobulin E levels fluctuate over time?
Yes, serum immunoglobulin E levels can fluctuate over time depending on factors such as exposure to allergens or infections, age, and overall health.