What Is Vitamin B9 Test
A Folate test is a blood test that measures the levels of Folate (also known as Vitamin B9) in the blood. It helps diagnose a deficiency in either of these vitamins, which can lead to anemia and other health problems. This test is commonly ordered as part of a routine blood test or to diagnose the underlying cause of anemia or other health issues.
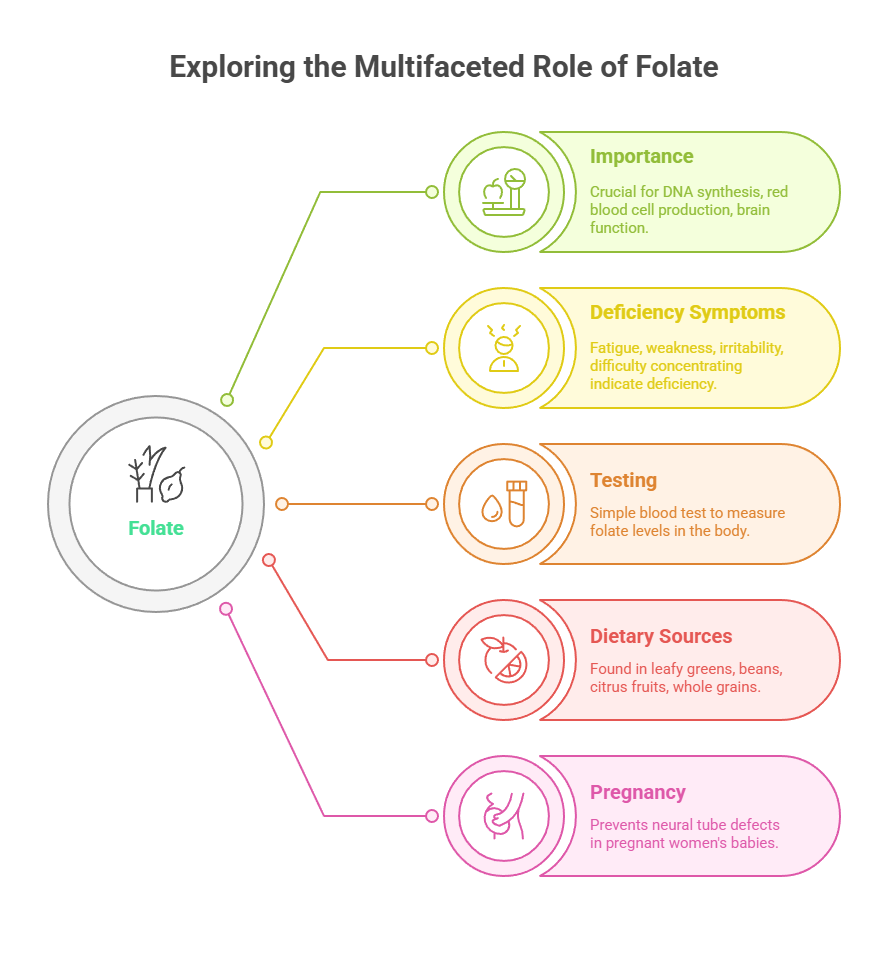
Folate (Vitamin B9) is an essential vitamin that plays a critical role in producing red blood cells, DNA synthesis, and proper brain function. Getting enough folate from a balanced diet or supplementation is essential, especially for pregnant women or those trying to conceive. A Folate test can help determine if you have a deficiency and if supplementation is necessary.
About Folate Test
Learn everything about the Vitamin B9 test by reading further.
Why Do I Need Folate Deficiency Test?
Folate is an essential nutrient required for many vital functions in the body, including the production of red blood cells, DNA synthesis, and brain function. Your doctor may order a folate test if you have folate deficiency (or B9 deficiency) symptoms, such as anemia, fatigue, or a weakened immune system.
A folic acid test can also help monitor the effectiveness of treatment for a folate deficiency or to assess your risk for certain health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease or congenital disabilities.
How to Prepare for Folic Acid Test?
There is no special preparation required for the Vitamin B9 Test. It is a simple blood test that requires drawing a blood sample from the vein in your arm. Before the test, be wary of the following factors:
- Do not fast unless prescribed by your healthcare professional.
- Drink adequate water before arriving at the diagnostic center.
- Avoid consuming alcohol or smoking.
- If you have medications, consult your healthcare provider to know if you can take those before getting your antibody levels checked.
What Happens During Folate Blood Testing?
Are you visiting your nearest diagnostic center to get your Folate test done? If yes, your healthcare professional will take the following steps to draw the blood sample:
- Your healthcare provider will wrap a thin pipe around your arm and cleanse the target area with rubbing alcohol.
- The expert will check for the vein in your arm and ask you to clench your fists tightly.
- Your healthcare provider will draw a blood sample from your vein using a syringe and collect it in a vial/test tube, removing the injection from your skin.
- They will seal the target area with a bandage to avoid bleeding and send your blood sample to the laboratory for testing.
- Usually, the vitamin B9 test will be available to you on the same day.
Finding Folate Test
Should you call for a Folate Test at home or get it done at your nearest clinic? Read more to find out what suits your comfort.
Can I Take B9 Deficiency Test at Home?
Yes, you can. You can contact your nearest diagnostic center to call a healthcare professional and get the folate blood test done from the comfort of your home.
How Much Does Folate Test Cost?
The vitamin 9 test price depends on the diagnostic center you choose to get it done. In most cases, insurance covers your folate test price, but if it doesn’t, it’s wise to purchase a new plan at affordable rates.
Test Results Interpretation
You undertook the test for folate and got your results. But you still need help determining if you have antibodies in the normal range. Read this section to understand how to go about your cancer diagnosis with your healthcare professional.
What Do Folate Test Results Mean?
If you’re wondering what your folate test results mean, here’s how you can understand them.
Low folate levels can indicate a deficiency, leading to health problems such as anemia, congenital disabilities, and damage to the nervous system. High folate levels can also indicate a health problem, such as liver disease or overconsumption of folic acid supplements.
It’s crucial to interpret the test results in the context of your overall health and in consultation with an experienced doctor, who can determine the best course of action based on the results.
What is Folic Acid Test Normal Range?
The usual range for folate levels in blood is between 3 and 20 ng/mL. The particular normal range, however, can vary based on the laboratory performing the test and the population being tested, thus it is always recommended to speak with a healthcare physician or refer to the reference range provided by the laboratory that did the test.
What Medical Conditions Can Elevated Folate Levels?
Some of the mentioned medical diseases can produce an increase in folate levels in the blood:
- When the liver is not working properly, folates can accumulate in the blood.
- Consumption of Alcohol can increase folate levels.
- Some cancers can produce prominent folate levels say colon and pancreatic cancer.
- Certain tumors, such as pancreatic and colon, can produce high quantities of folate.
- Anticonvulsants and methotrexate are some drugs that can have an effect on folate levels.
What Medical Conditions Can Cause Low Folate Levels?
Your folate levels can decrease due to the following medical conditions:
- Anemia: Folate is required to produce red blood cells, and folate deficiency can trigger megaloblastic anemia, where the red blood cells produced are large and abnormal, leading to fatigue and weakness.
- Neural Tube Defects: Folate is vital for proper brain development. A deficiency during pregnancy can increase the risk of congenital disabilities (birth defects), including neural tube defects.
- Cognitive Impairment: A long-term deficiency in folate can lead to cognitive impairment, including memory loss and confusion.
- Depression: Low folate levels have been associated with an increased risk of depression and mood disorders.
Why Choose HealthcareOnTime
Convenience at Your Doorstep
Ever wished for healthcare that comes to you? HealthcareOnTime makes it a reality with doorstep lab testing, cutting out clinic hassles. No more queues or travel stress. Experience at-home sample collection, prioritizing health without time constraints. —your path to health, now just a doorstep away!
Affordable Testing with Thyrocare Partnership
Experience cost-effective lab testing at-home with HealthcareOnTime’s exclusive partnership with Thyrocare. Benefit from competitive prices while ensuring precise results. Our collaboration with Thyrocare Technologies Limited guarantees affordability without compromising on the accuracy and reliability of your lab test.
Comprehensive Health Screening
At HealthcareOnTime, we’ve got your back with our comprehensive health checkup packages! Take charge of your well-being by booking online. These packages empower you to stay ahead, catching potential issues early for timely management. It’s like having a health ally, and making informed decisions for a healthier, happier life.
Ref Links:
More Related Tests
Why To Book with HealthCareOnTime
17 Crores+ Samples Processed
World Class Technology Labs

25+ Years of Trust & Experience

Free Home Collection
FAQs Around Vitamin B9 (Folate Test)
What happens if folic acid is high?
High levels of folic acid in the blood can signify certain medical conditions or an overdose of folic acid supplements. It can also interfere with the effectiveness of certain medications, such as anticonvulsants.
What are the symptoms of low folate?
Low folate levels (vitamin B9) can cause symptoms like fatigue, weakness, gray hair, mouth sores or tongue swelling, diarrhea, loss of appetite, weight loss, irritability, mental confusion, depression, forgetfulness, and congenital disabilities (when a deficiency occurs during pregnancy).
What is a low folate level?
If your test results are below 3 ng/mL, it can be indicative of low folate levels.
What happens if folate deficiency is left untreated?
An untreated folate deficiency can lead to several healthcare issues, including anemia, cognitive and psychological problems, heart disease, a weak immune system, and cancer.
What is a normal folate level for a woman?
A normal folate level for a woman is typically considered to be in the range of 4.0 to 18.0 ng/mL.
What do folate levels indicate?
Folate levels indicate the amount of folic acid in a person’s blood. Low folate levels can indicate a deficiency, leading to problems with red blood cell production & neural tube defects in a developing fetus. High folate levels can indicate the presence of liver disease or certain types of cancer.