What Is FBS Test
Blood glucose level is the key source of your body’s energy and it helps you stay active, productive and energetic. However, any fluctuations whether permanent or temporary in its level can put you at a higher risk of developing Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes and a host of other allied health complications. A fasting blood sugar test or FBS test aims at measuring the glucose level in your bloodstream when it’s expected to stay minimal. A fasting sugar test usually requires you to fast for at least 8 to 12 hours. A fasting glucose test is a crucial tool to identify diabetes, prediabetes and gestational diabetes.
This glucose testing modality helps your healthcare provider assess whether you already have diabetes, are prediabetic or the amount of risk you are at developing Type 2 diabetes. If your healthcare provider suspects you to be at a risk of Type 1 diabetes, you will also be recommended to get tested for autoantibodies and ketones, which confirm an impaired glucose tolerance and insulin resistance in your body.
About FBS Blood Test
Learn everything about fasting blood sugar test before you book lab test online. Understand the why, how, and what of this test.
Why Do I Need Fasting Blood Sugar Test?
Your healthcare provider may recommend a FBS test as part of your routine metabolic panel checks. You will also be asked to opt for a test if
- You exhibit symptoms of abnormally high or low fasting blood glucose levels
- You are experiencing sudden surges in urination, thirst, hunger and fatigue as a response to high glucose levels in your bloodstream.
- You are experiencing excessive shaking, sweating, jitters, lack of energy, and concentration, fast or irregular heartbeats as a result of extremely low levels of blood sugar.
- You are pregnant, which puts you at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes.
- You have a past history of high fasting glucose levels.
- You have risk factors for diabetes and other sugar-led health complications.
How To Prepare For Fasting Blood Sugar Testing?
To prepare for FBS Testing, follow these steps: Consult your healthcare provider, inform them about medications, avoid intense exercise, follow fasting instructions of 8 to 12 hours typically overnight, avoiding all food and drinks except water or as suggested by your healthcare provider and provide accurate medical history.
What Happens During FBS Blood Testing?
FBS Blood Testing only takes a few minutes.
- As per the scheduled time of the blood test, a lab technician who usually takes blood samples will arrive.
- A thin needle will be used to draw blood from your arm’s vein.
- The needle might cause a mild pinch and some discomfort.
- The lab technician then fills a collection tube with blood and then removes the needle from the skin.
- They place a small bandage on the arm.
Finding FBS Blood Test
Should you book blood test online to check your fasting blood sugar level or go to the nearest clinic and get it done by a medical professional? Let’s Find Out
Can I Take FBS Level Test At Home?
Yes, the fasting Sugar Test can be taken at home. HealthcareOnTime’s at-home lab testing service in association with Thyrocare, provides a convenient and efficient way to get important medical tests done from the comfort of your place, without the need for a doctor’s visit or a trip to a lab. It is always preferable to consult with a healthcare provider about any concerns regarding your test results.
How Much Does FBS Test Cost?
Are you curious about the FBS test price? At HealthcareOnTime, we believe in providing cost-effective solutions to keep you informed about your blood sugar levels.
The fasting blood sugar test price can vary depending on several factors, including your location, the healthcare provider, and your insurance coverage. However, we’re pleased to offer this essential test at an affordable rate of just INR 80! Our prices not only compete in the market but also maintain the highest quality standards.
In India, the cost of an Fasting Blood Sugar test typically starts from INR 200, but prices may vary based on the specific laboratory and city. Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial, especially if you have diabetes or are at risk of developing it.
But here’s the exciting part – HealthcareOnTime is committed to making healthcare accessible to all. We provide an impressive up to 20% discount on FBS testing in India. This valuable service is made possible through our trusted partner, Thyrocare, and is available in over 4500+ pincodes nationwide.
You can also explore our extensive range of blood sugar testing options and diabetes management Test packages at HealthcareOnTime.
| Test/Package Name | Price (INR) |
| 2000 | |
| 1000 | |
| 500 | |
| 400 | |
| 300 | |
| 149 | |
| 150 |
Test Result Interpretation
You received your FBS test results but still need help determining if they fall under the normal range. Read this section to understand whether your results are within the fasting sugar normal range or not.
What Does FBS Test Results Mean?
The result of the fasting glucose test essentially depends on the contents of your last meal, size of your last meal and your body’s response to internal insulin production and functioning. A higher fasting blood sugar level, which is beyond 126 mg/dL, indicates that you have diabetes. High fasting sugar levels can also be caused due to eating large meals with sugary foods and drinks with simple carbohydrates. While a lower FBS test value is desired, anything below 99 mg/dL might be caused due to diabetic medications and indicate other underlying health conditions.
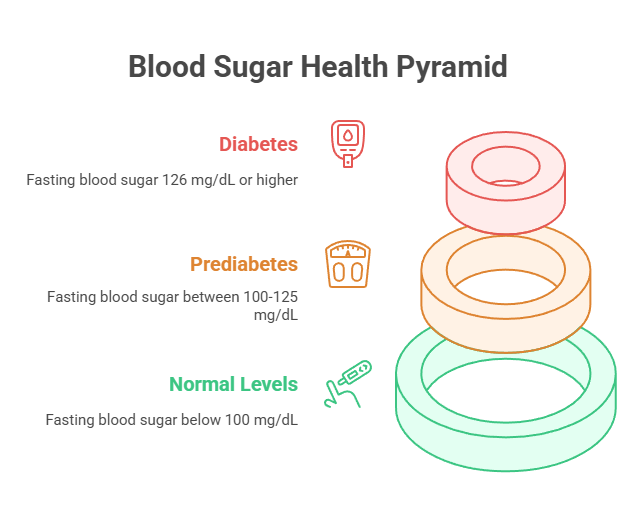
What Is Fasting Blood Sugar Normal Range?
99 mg/dL is considered the fasting glucose normal range and anything beyond this is deemed a higher fasting blood sugar normal value.
| Fasting Blood Glucose Level | Remarks |
| 55 mg/dL or less | Very low |
| 99 mg/dL or less | Normal |
| 100 to 125 mg/dL | Prediabetes |
| 126 mg/dL or more | Diabetes |
[Source]
Seek the right preventive and treatment measures and opt for healthier lifestyle choices for attaining normal fasting blood sugar levels.
What Medical Conditions Can Cause High FBS Levels?
Medical conditions responsible for your very high fasting sugar level are:
- Overactive Thyroid Gland – In this instance, because of too much of thyroid hormones, insulin gets discarded from your body fast, which impacts the glucose transportation in your body. Glucose gets accumulated in your bloodstream leading to higher than normal fasting blood sugar levels.
- Pancreatic cancer – Due to this, islets in your body don’t produce insulin as a response to insulin resistance. This can lead to Type 3c diabetes, which is known as pancreatic diabetes.
- Pancreatitis – Swelling or inflammation of the pancreas disrupts the insulin functionality, leading to high glucose levels.
- Unmanaged stress
- Pheochromocytoma – This is a rare tumour that may cause metabolic derangement and impaired glucose tolerance, leading to high fasting glucose levels.
- Acromegaly – This tumour may cause hepatic and peripheral insulin resistance leading to high blood sugar levels.
- Cushing Syndrome – This medical condition occurs due to high cortisol hormones, which is known to raise the blood pressure and glucose levels.
- Glucagonoma – This pancreatic alpha-cell tumour tends to secret glucagon, which is linked with raised blood sugar levels.
A test result that is beyond the normal FBS range might often indicate more health complications than just diabetes. Do opt for periodic FBS testing to stay vigilant and seek on-time diagnosis, prevention and treatment interventions.
What Medical Conditions Can Cause Low FBS Levels?
Your fasting blood sugar level can be lower than the optimal range due to medical conditions, such as:
- Hypopituitarism – Deficiency of one or more pituitary hormones.
- Underactive Thyroid or Adrenal Gland Insufficiency – Affects the insulin production and functionality.
- Insulinoma – Referred to as tumours in the pancreas, which ultimately affects the insulin production and its operational efficiency.
- Liver Diseases – Liver conditions, such as hepatitis or Liver cirrhosis, can disrupt the liver’s ability to regulate glucose, potentially resulting in lower fasting blood sugar levels.
- Kidney Diseases – Kidney problems can impact glucose metabolism, causing fluctuations in blood sugar levels, including lower fasting blood sugar levels.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Other hormonal imbalances, not just those related to the pituitary, thyroid, or adrenal glands, can affect blood sugar regulation and cause hypoglycemia.
Lifestyle factors, such as less food consumption, higher dosage of diabetes medications or insulin, considerable weight loss as a result of weight loss surgery, vigorous exercise can lead to abnormally low fasting glucose levels.
Why Choose HealthcareOnTime?
Convenience at Your Doorstep
Ever wished for healthcare that comes to you? HealthcareOnTime makes it a reality with doorstep lab testing, cutting out clinic hassles. No more queues or travel stress. Experience at-home sample collection, prioritizing health without time constraints. —your path to health, now just a doorstep away!
Affordable Testing with Thyrocare Partnership
Experience cost-effective lab testing at-home with HealthcareOnTime’s exclusive partnership with Thyrocare. Benefit from competitive prices while ensuring precise results. Our collaboration with Thyrocare Technologies Limited guarantees affordability without compromising on the accuracy and reliability of your lab test.
Comprehensive Health Screening
At HealthcareOnTime, we’ve got your back with our comprehensive health checkup packages! Take charge of your well-being by booking online. These packages empower you to stay ahead, catching potential issues early for timely management. It’s like having a health ally, and making informed decisions for a healthier, happier life.
Disclaimer: Although we have endeavoured to provide accurate information on this page, we strongly recommend that you seek advice from your doctor before relying on any of the test ranges or lab-test recommendations mentioned herein.
Sources
Ref Links:
More Related Tests
Why To Book with HealthCareOnTime
17 Crores+ Samples Processed
World Class Technology Labs

25+ Years of Trust & Experience