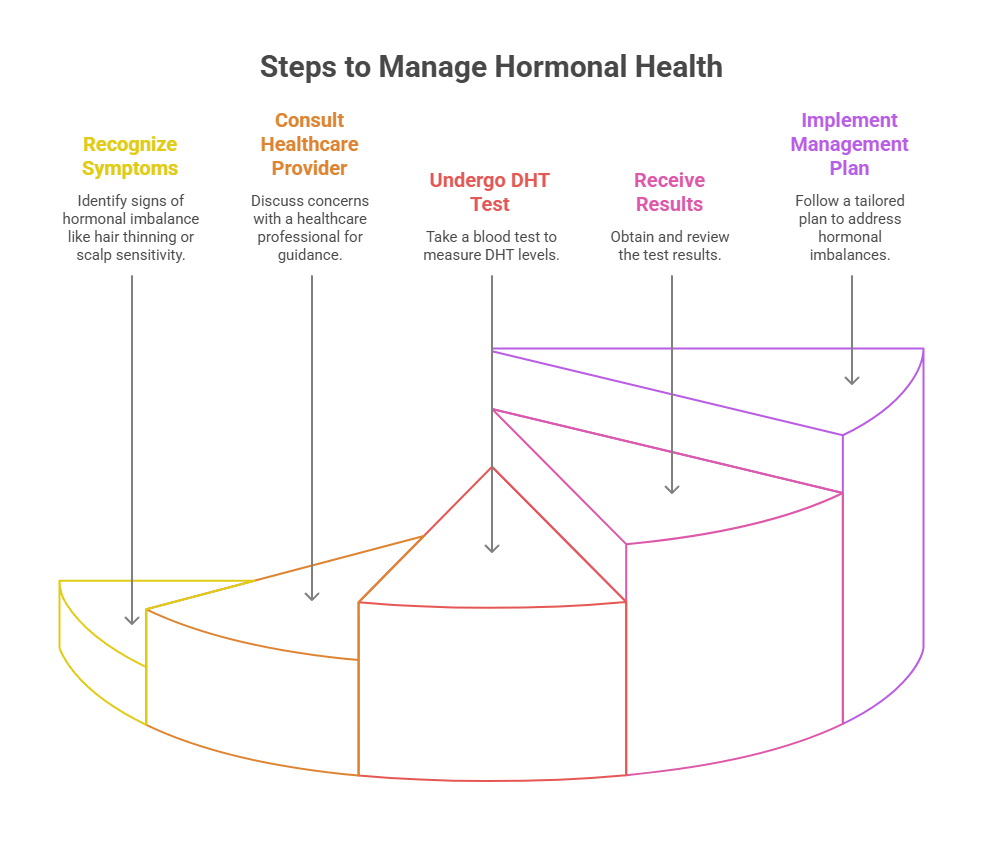
What Is Dihydrotestosterone Test (DHT)?
A DHT Level test measures the level of dihydrotestosterone hormone in the blood to assess the risk of occurrence of Androgenic Alopecia. Increased DHT is one of the key causes of Androgenic Alopecia and most identified males with pattern baldness tend to have a high DHT-to-testosterone ratio and androgen receptor activities in the hair follicles. You will be recommended to undergo this blood test for hair loss if you are exhibiting any signs of male pattern baldness or your healthcare provider thinks you are at risk of developing it.&nb-sp;
What is DHT and What Does It Do?
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a hormone crucial for the development of sexual structures and characteristics in individuals assigned to males at birth (AMAB) 1. As an androgen, it stimulates the development of male traits throughout life, starting from foetal development. While its effects on individuals assigned female at birth (AFAB) are not fully understood, it may influence body and pubic hair growth.
DHT, derived from testosterone, contributes to male sex characteristics during puberty, such as a deep voice, increased body hair, and muscle mass, and growth of reproductive organs. It also helps regulate fat distribution and supports overall muscle mass, sexual health, and fertility.
In adults, the enzyme 5-alpha reductase converts about 10 percent of testosterone to DHT. The DHT can bind to receptors on scalp hair follicles, leading to hair loss. Elevated DHT levels have also been linked to slow skin healing, enlarged prostate, prostate cancer, and coronary heart disease.2
For older adults, DHT is associated with prostate enlargement and Androgenic Alopecia (male pattern baldness), which is recognised with the symptoms of bald spots on the top and frontal scalp regions. While Androgenic Alopecia is mostly associated with males, females also struggle with DHT-induced female pattern baldness.
What Causes DHT to Increase?
Normal DHT levels in males and females are highly desired. However, there are certain factors and medical conditions that can trigger high DHT levels. Here are a few of them:3
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals are genetically predisposed to higher levels of 5-alpha-reductase enzyme activity. This enzyme is crucial for the conversion of testosterone to DHT. An increased enzyme activity would naturally lead to higher DHT levels. For instance, men with male androgenic alopecia (MAA) have been found to have higher levels of 5-alpha-reductase activity in their scalp hair follicles.
- Increased testosterone levels: Since DHT is synthesized from testosterone through the action of the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme, any condition or factor that leads to an increase in testosterone levels can potentially raise DHT levels as well. This is because more substrate (testosterone) is available for conversion into DHT.
- Increased activity of 5-alpha-reductase enzyme: Any factor that increases the activity of the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme will lead to an increase in DHT levels. This includes certain medications, dietary factors, and perhaps even lifestyle factors that have yet to be fully understood.
- Changes in hormone regulation: Conditions that alter the normal regulation of hormones, including but not limited to, pcod problem in women, could indirectly affect DHT levels through complex endocrine pathways involving testosterone and other androgens.
- Resistance to 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors: In the context of treatment, particularly for conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer, the use of 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors is aimed at reducing DHT levels. However, resistance or incomplete inhibition could lead to situations where DHT levels are not adequately controlled.
You should opt for DHT Level test as recommended by your healthcare provider to gauge your blood DHT levels. Choose HealthcareOnTime to avail DHT test at home in an easy, seamless, and hassle-free manner.
About DHT Blood Test
Learn everything about the DHT Profile Test, before you book lab test online. Understand the why, how, and what of this test.
What Does the DHT Test For Hair Loss Measure?
The DHT Level test measures the levels of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) in the blood, aiding in identifying the cause of conditions like male pattern hair loss, prostate issues, excess androgen production leading to virilization, Genetic Hair Loss, infertility, hirsutism, or amenorrhea.
It is particularly useful for diagnosing 5-alpha-reductase deficiency, indicated by an elevated testosterone-to-DHT ratio, and is crucial for screening for prostate cancer. This test requires no fasting and is conducted when concerns about these health issues arise, offering insights into the hormonal balance related to DHT.
What Happens When DHT Levels Are Low?
Normal DHT levels in males play a pivotal role in ensuring the appropriate onset of puberty and the development of reproductive organs. Lower than normal DHT levels identified as part of the DHT blood test may mean that individuals may experience the following effects on the body: 4
- Low DHT may cause delays in the onset of puberty for both males and females.
- In males, it can lead to incomplete development of sex organs, such as the penis and testes, as well as reduced pubic and body hair.
- DHT plays a role in the growth and maintenance of the prostate.
- Reduced DHT levels may contribute to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) due to increased growth of prostate cells.
What Happens When DHT Levels Are High?
More than the normal levels of DHT level test when the identified result is deemed as an unfavourable outcome. High DHT levels are often associated with hair loss in males and females. Apart from hair
loss, hair thinning and pattern baldness, high DHT levels may cause white hair at a young age, too.
When DHT levels are high, it can lead to several health conditions, including:5
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH): High levels of DHT can stimulate prostate growth, leading to BPH. This condition is common in individuals assigned male at birth (AMAB) over the age of 50 and can cause urinary difficulties and sexual dysfunction.
- Prostate Cancer: Elevated DHT activity in the prostate, along with certain genetic mutations, can contribute to the development of prostate cancer. Increased DHT levels are often observed in individuals with prostate cancer.
- Androgenic Alopecia: High DHT activity at hair follicles can contribute to male pattern hair loss, also known as androgenic alopecia. This condition results in hair loss, typically at the top and frontal regions of the scalp, leading to a receding hairline.
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): In individuals assigned female at birth (AFAB), high DHT levels can result from excess testosterone production associated with PCOS. This hormonal imbalance can lead to symptoms such as irregular periods, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), and acne.
Why Do Doctors Recommend a Dihydrotestosterone Test?
Your healthcare provider will recommend you to undergo a dihydrotestosterone test:
- You are exhibiting signs of Androgenic Alopecia (male pattern hair loss) or are at a higher risk of developing it due to genetics and family history.
- You are exhibiting signs of prostate enlargement, Benign Prostate Hyperplasia or prostate cancer and are at risk of developing the same.
- You have coronary artery disease. High DHT levels are often associated with CAD and other cardiovascular disorders.
- You have 5-Alpha-Reductase deficiency. This is an autosomal recessive condition mostly found in male infants with symptoms, such as underdeveloped genitalia, undescended functional testes, and an incomplete or dysfunctional prostate.
- You have androgen deficiencies and your healthcare provider is looking at DHT hormone therapy as a potential treatment option.
- In each of these scenarios, a DHT blood test can provide valuable information to guide diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring of various health conditions.
How To Prepare For DHT Blood Test?
The steps below help you ensure that your DHT blood test provides the most accurate information about your health.
- Medication guidelines: Tell your healthcare provider about all the drugs, supplements or herbal remedies you are taking, as some substances may affect test results. Follow any specific instructions regarding drug adjustment before testing.
- Contact to doctor: Share your entire medical history with existing health conditions or symptoms to help explain test results.
What Happens During DHT Testing?
A Dihydrotestosterone Test only takes a few minutes.
- As per the scheduled time of the blood test, a Lab Technician who usually takes blood samples will arrive.
- A thin needle will be used to draw blood from your arm’s vein.
- The needle might cause a mild pinch and some discomfort.
- The lab technician then fills a collection tube with blood and then removes the needle from the skin.
- They place a small bandage on the arm
- The blood sample collected for the DHT test is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. In the lab, technicians will measure the concentration of a specific compound: dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Please note: There might be slight pain or bruising at the spot of insertion, but most of the symptoms go away quickly.
How Often Is a DHT Test For Hair Loss Required?
There is no definite frequency for DHT hormone tests. Some individuals might not even need a DHT test throughout their lives. If you or your loved ones are experiencing any symptoms associated with high or low DHT levels, you may opt for periodic screenings as recommended by your healthcare provider.
Finding a DHT Blood Test
Should you call for the blood test at home to check your DHT levels or get it done by a medical professional at your preferred nearest clinic?
Can I Take a DHT Test At Home?
Yes, the DHT blood testing can be taken at home. HealthcareOnTime’s at-home lab testing service in association with Thyrocare, provides a convenient and efficient way to get important medical tests done from the comfort of your place, without the need for a doctor’s visit or a trip to a DHT lab test. It is always preferable to consult with a healthcare provider about any concerns regarding your test results.
How Much Does a DHT Hormone Test Cost?
The DHT Hormone Test cost varies significantly depending on many factors.
- Location: DHT blood Test Price may vary depending on the city or the region in which the test is conducted. For example, in Bangalore or Mumbai, it might be expensive as compared to small towns.
- Type of facilities centres: The DHT test price also varies between private hospitals, government hospitals, and diagnostic centres. DHT test price is lower in government hospitals as compared to private ones.
- Healthcare centres: Diagnostic centres, laboratories and hospitals may have different DHT quantitative test prices. It depends upon the benefits and reputation of the healthcare centre.
- Insurance Coverage: Individuals with health insurance can cover partial or all costs depending on their policy coverage and network providers.
- Other tests: DHT is not included in larger panel of tests. The overall cost may vary depending on the number and type of tests included in the panel.
- Additional services: Additional services such as home sample collection, express test results, or additional charges for special management may be paid, which contributes to the overall DHT test cost.
Excitingly, HealthcareOnTime is committed to making healthcare accessible to all. We’re pleased to offer DHT hormone test costs at just INR 970! Our prices compete in the market while maintaining the highest quality standards.
You can also explore our extensive range of hormone imbalance tests options and related hair screening packages at HealthcareOnTime.
| Test or Package | Price (INR) |
| Starts at 390 | |
| Starts at 390 | |
| 2749 | |
| 2749 |
Test Result Interpretation
You received your DHT test results but still need help determining if they fall under the normal range. Read this section to understand whether your results are within the DTH normal range or not.
What do the DHT Test Results Mean?
The DHT level test is primarily recommended for assessing the occurrence or risk of Androgenic Alopecia and other male sexual development-related concerns. High DHT levels may indicate Male Pattern Baldness, prostate enlargement, Benign Prostate Hypertrophy, and Hirsutism.
Low DHT levels as a result of a DHT blood test might indicate delayed sexual development during puberty in males, delayed or incomplete development or functioning of reproductive organs, Gynecomastia (female-like breasts), prostate tumours and other sexual dysfunction.
Even though there is a change in DHT levels by age, if your DHT hormone test results vary from the normal range, consult with your healthcare provider to arrive at a conclusive diagnosis and seek on-time treatment/prevention.
What Is The DHT Test Normal Range?
The DHT normal range varies for males and females and also with progressive ageing. While the normal DHT levels in males may range between 50 and 955 pg/mL as per age, the normal DHT levels in females vary between 50 pg/mL to 300pg/mL due to age differentiation.6
DHT Levels by Age
Normal DHT levels vary by age in both males and females. The normal DHT test ranges are as follows:
Normal DHT Levels in Male
| Tanner Stage/ Age | Age (Males) | Normal DHT Level in Males (pg/mL) |
| Infants | ≤6 months | ≤1,200 |
| Tanner Stage I (>6 months and prepubertal) | 7.1 Year | ≤50 |
| Tanner Stage II | 12.1 Years | ≤200 |
| Tanner Stage III | 13.6 Years | 80 – 330 |
| Tanner Stage IV | 15.1 Years | 220 – 520 |
| Tanner Stage V | 18 Years | 240 – 650 |
| Over 19 years of Age | > 19 years | 112-955 |
Normal DHT Levels in Female
| Tanner Stage/ Age | Age (Females) | Normal DHT Level in Female (pg/mL) |
| Infants | ≤6 months | ≤1,200 |
| Tanner Stage I (>6 months and prepubertal) | 7.1 Year | ≤50 |
| Tanner Stage II | 10.5 Years | ≤300 |
| Tanner Stage III | 11.6 Years | ≤330 |
| Tanner Stage IV | 12.3 Years | ≤330 |
| Tanner Stage V | 14.5 Years | ≤330 |
| Between 20 to 55 years of age | 20 – 55 Years | ≤300 |
| Over 55 years | >55 years | ≤128 |
You can also explore our extensive range of hormone imbalance test options and related hair screening packages at HealthcareOnTime.
What Medical Conditions Can Cause High DHT Levels?
If your DHT blood test results reveal a higher-than-normal DHT level, your healthcare provider will further assess your risks of developing 7:
- Androgenic Alopecia8 – Androgenic Alopecia is a prominent type of hair loss mostly observed in ageing males and is often linked with hyperactivity of DHT hormones and androgen receptor activities at the hair follicle roots. Hair loss happens as patches of bald spots on the frontal and top regions of the scalp, which recede with time. High DHT levels tend to shrink the hair follicles and reduce the hair growth cycle and thus contribute towards male pattern baldness.
- Benign Prostate Hyperplasia9 – It is a condition in which the prostate gland enlarges beyond its usual growth and impacts the urethra. The urinary bladder wall tends to become thicker and eventually weakens and loses its ability to eliminate body waste through urine.
- Prostate Cancer – High DHT levels result in uncontrolled genetic proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis related to DHT pathways.
- PCOS – Though DHT is often linked with male reproductive disorders and pattern baldness, female physiology has also been linked, especially to females with PCOS conditions. It is recognised with symptoms, such as excessive body weight, fat, serum cholesterol levels, etc.
What Medical Conditions Can Cause Low DHT Levels?
If your DHT hormone test results reveal a less-than-normal DHT level, you might have 10:
5-Alpha-Reductase Deficiency – This condition is associated with low levels of DHT hormone and often accompanies symptoms, such as underdeveloped and dysfunctional or partially functional reproductive organs and prostate. In chronic cases, male children might have female-like genitalia. At the onset of puberty, they may suffer a lack of facial hair and female-like pubic hair growth too.
Male Hypogonadism – Otherwise known as a condition in which the testosterone hormone levels are typically lower than normal, this condition is an indicator of low DHT levels. Since testosterone hormones get converted into DHT, a low level of testosterone means a low level of DHT.
Sources
Ref Links:
- DHT (Dihydrotestosterone)
- What You Need to Know About DHT and Hair Loss
- Biochemistry, Dihydrotestosterone
- How Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) Causes Hair Loss
- DHT (Dihydrotestosterone)
- Dihydrotestosterone, Serum
- DHT (Dihydrotestosterone)
- Androgenetic alopecia
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
- DHT (Dihydrotestosterone)
More Related Tests
Why To Book with HealthCareOnTime
17 Crores+ Samples Processed
World Class Technology Labs

25+ Years of Trust & Experience

Free Home Collection
FAQs Around Dihydrotestosterone Test (DHT)
Will reducing DHT regrow hair?
Reducing DHT (dihydrotestosterone) levels can slow down hair loss and sometimes promote regrowth. Medications like finasteride are commonly prescribed to inhibit DHT production, but results vary among individuals. It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice on hair loss treatment options, as they can assess your specific situation and recommend the most suitable approach.
How can I control DHT naturally?
Natural methods to control DHT include maintaining a well-balanced diet rich in nutrients like zinc and saw palmetto, which may help reduce DHT production. Regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can also contribute to DHT regulation. However, it’s essential to note that the effectiveness of these natural methods can vary among individuals, and consulting a healthcare provider is advisable to develop a personalized strategy.
Can high DHT be cured?
High DHT levels can be managed but not completely cured. Medications like finasteride and dutasteride can lower DHT levels, particularly in the context of conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and male pattern baldness. Lifestyle changes, such as a healthier diet and stress reduction, can also help control DHT production. However, it’s essential to understand that these approaches aim to manage DHT and its associated conditions rather than eliminate it entirely. Consultation with a healthcare professional is crucial to assess your specific situation and determine the most appropriate treatment or management plan.