What is ASO Test?
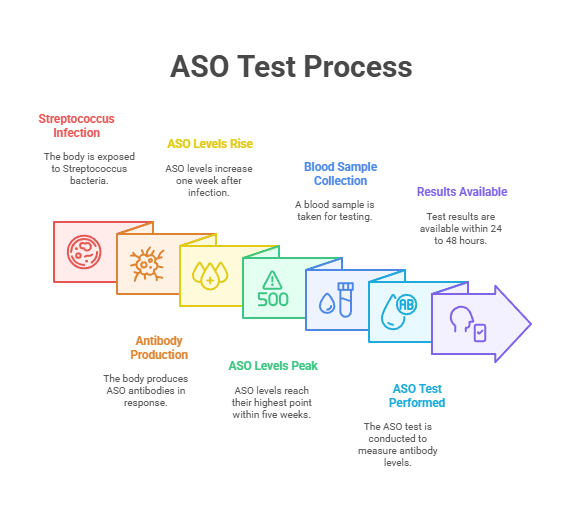
The Antistreptolysin O (ASO) test is a diagnostic tool used to measure the level of antibodies called Antistreptolysin O in the blood. When your body gets exposed to the group of Streptococcus bacteria, after the first week and up to several weeks following the infection.
What is antistreptolysin o?
Your body produces antibodies as a response to fight off the bacterial intrusion and the Streptolysin toxins produced by the bacteria. These antibodies are referred to as Antistreptolysin O.
Streptococcus pyogenes, commonly known as group A Streptococcus is responsible for various infections, including strep throat, scarlet fever, and certain skin infections. By evaluating the ASO Titre, healthcare professionals can assess the body’s immune response to the streptococcal infection.
It’s worth mentioning that ASO levels can rise and fall relatively quickly after a streptococcal infection, so the timing of the test is crucial for its accuracy. If a person has had a streptococcal infection in the past, their ASO levels may remain elevated for a more extended period, even after the infection has been successfully treated.
About ASO Blood Test
Learn everything about Antistreptolysin O Test (ASO Titre) before you book your blood test online. Understand the why, how, and what of this test
Why Do I Need an ASO Titre Test?
ASO Titre Blood Test might not help your healthcare provider diagnose a current Strep infection as antibodies require time to be produced and this time window may vary from individual to individual.
Your healthcare provider will recommend an Antistreptolysin O Test if:
- You are exhibiting symptoms of a recent Streptococcal infection
- You are exhibiting symptoms of post-streptococcal complications, such as Bacterial Endocarditis, Glomerulonephritis, Rheumatic Fever, etc.
- You have complications, such as infections of the sinuses, tonsils, skin, middle ear and blood
- Your child under the age of 15 years is exhibiting signs of scarlet fever, such as sunburn-like red rashes, red lines across the groin, armpits, elbows, knees, and neck, red and bumpy tongues, and a flushed face
- There are symptoms of Rheumatic fever, such as tender and painful joints, excessive fatigue, uncontrollable jerking movements, chest pain, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat, etc.
- There are symptoms of Glomerulonephritis, such as hematuria, fatigue, nausea, hypertension, swelling in the face and joints, pain in the abdomen, etc.
ASO Titre test results may vary based on your health history, when the infection occurred and when the testing was conducted. ASO blood test thus should be conducted along with other diagnostic measures, such as throat culture or rapid antigen tests, which may be performed in conjunction with the ASO test to provide a comprehensive assessment of the infection and to identify the underlying health complications and recommend the future course of treatment, prevention and management.
How To Prepare for ASO Blood Test?
For a lab diagnosis of streptococcus pyogenes, fasting is typically not required. Consult your healthcare provider for specific instructions. Additionally, inform your provider about medications, avoid intense exercise, and provide a comprehensive medical history for a thorough assessment of your metabolic health.
Finding ASO Blood Test
Should you book blood test online to check your ASO levels or go to the nearest clinic and get it done by a medical professional? Let’s Find Out
Can I Take ASO Test At Home?
Yes, the ASO Blood testing can be taken at home. HealthcareOnTime’s at-home lab testing service in association with Thyrocare, provides a convenient and efficient way to get important medical tests done from the comfort of your place, without the need for a doctor’s visit or a trip to a lab. It is always preferable to consult with a healthcare provider about any concerns regarding your test results.
How Much Does ASO Test Cost?
Are you curious about the ASO test price and its role in detecting streptococcal infections? At HealthcareOnTime, we prioritize cost-effective solutions, providing crucial insights into your ASO levels for identifying streptococcal infections.
The ASO titre test cost can vary based on factors like your location, healthcare provider, and insurance coverage. However, we’re pleased to offer this important test at an affordable rate of just INR 585! Our prices remain competitive in the market while upholding the highest quality standards.
In India, the ASO test price typically starts at INR 800, varying by the laboratory and city. Staying informed about your ASO levels is crucial for proactive management of streptococcal infections.
Excitingly, HealthcareOnTime is committed to making healthcare accessible to all. We provide valuable services, including Antistreptolysin O Titre testing, in over 4500+ pin codes. Your health matters, and we’re here to make quality healthcare, incorporating comprehensive ASO measurements, convenient and affordable.
Test Result Interpretation
You’ve received your ASO Test results, but you may still be uncertain about whether they fall within the normal range. Continue reading this section to gain clarity on whether your results are within the expected range or not.
What Does ASO Blood Test Results Mean?
The ASO Test normal range [1] for adults is considered 200 and for children under the age of 5 years, it can be 100. The ASO titre normal range (ASO) levels can vary among different laboratories, and the values may depend on the specific testing method used.
Wondering about what happens if ASO titre is high? Well, The ASO Titre blood test results might be higher than the ASO Titre normal range if you have had a recent streptococcal infection, which typically means you are ASO titre positive. The ASO levels tend to spike during the 3rd to 8th week after the streptococcal infection and may decline after that.
Some individuals might not exhibit readily identifiable symptoms of streptococcus infections and post-streptococcal complications. So, Antistreptolysin O Titre tests need to be conducted repeatedly within 10 to 14 days to arrive at a conclusive diagnosis.
What Conditions Can Cause High ASO Blood Levels?
The result, which is higher than the ASO Titre test normal range, might be caused due to a recent streptococcal infection.
Some conditions that can cause high ASO blood levels include:
- Strep Throat: This is a common bacterial infection that primarily affects the throat and tonsils. If left untreated, it can lead to potential complications, such as rheumatic fever or kidney inflammation. The ASO Titre Blood test can help diagnose and monitor the progress of strep throat.
- Scarlet Fever: This is a streptococcal infection that causes a distinctive rash along with a sore throat and high fever. The ASO test can aid in confirming the diagnosis of scarlet fever and assessing the severity of the infection.
- Rheumatic Fever: This is a rare but serious complication that can occur after a strep throat or scarlet fever infection. It affects the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The ASO test can be useful in diagnosing rheumatic fever and monitoring its progression.
- Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis: This is a kidney disease that can develop after a strep throat or skin infection caused by streptococcus. The ASO test helps in identifying the presence of streptococcal infection and monitoring kidney function.
Your healthcare provider will recommend a rapid streptococcal antigen test or a throat culture if you are suspected of having throat-related complications as an aftereffect of untreated Streptococcal infection.
Anti-DNAse B, anti-hyaluronidase, or anti-streptophyte are some of the other potent antibody tests that your healthcare provider will recommend along with the ASO blood test to assess Rheumatic fever, Glomerulonephritis, and other conditions.
What Conditions Can Cause Low ASO Blood Levels?
Lower than the ASO titre normal range means that your streptococcal infection symptoms are declining. However, periodic ASO tests should be conducted to ensure no ill effects of the bacterial infection linger.
What Are Some Other Tests You May Need With an ASO Titre?
While the ASO Titre Blood Test is valuable in assessing streptococcal infections and related complications, additional tests may be required for a comprehensive evaluation. These tests may include:
- Throat Culture: A throat culture involves swabbing the throat to obtain a sample for laboratory analysis. It helps identify the specific strain of streptococcus causing the infection and guides appropriate treatment.
- Rapid Antigen Tests: These tests provide quick results by detecting specific streptococcal antigens in the throat. They are often used in conjunction with the ASO Titre test to confirm the presence of an active streptococcal infection.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC test measures various components of the blood, including white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. It can help identify any abnormal changes associated with a streptococcal infection.
- Kidney Function Tests: If there are concerns about kidney involvement, such as in post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, additional tests to assess kidney function, such as blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine serum test, may be ordered.
Why Choose HealthcareOnTime
Convenience at Your Doorstep
Ever wished for healthcare that comes to you? HealthcareOnTime makes it a reality with doorstep lab testing, cutting out clinic hassles. No more queues or travel stress. Experience at-home sample collection, prioritizing health without time constraints. —your path to health, now just a doorstep away!
Affordable Testing with Thyrocare Partnership
Experience cost-effective lab testing at-home with HealthcareOnTime’s exclusive partnership with Thyrocare. Benefit from competitive prices while ensuring precise results. Our collaboration with Thyrocare Technologies Limited guarantees affordability without compromising on the accuracy and reliability of your lab test.
Comprehensive Health Screening
At HealthcareOnTime, we’ve got your back with our comprehensive health checkup packages! Take charge of your well-being by booking online. These packages empower you to stay ahead, catching potential issues early for timely management. It’s like having a health ally, and making informed decisions for a healthier, happier life.
Disclaimer: Although we have endeavoured to provide accurate information on this page, we strongly recommend that you seek advice from your doctor before relying on any of the test ranges or lab-test recommendations mentioned herein.
More Related Tests
Why To Book with HealthCareOnTime
17 Crores+ Samples Processed
World Class Technology Labs

25+ Years of Trust & Experience

Free Home Collection
FAQs Around Antistreptolysin O Test (ASO Titre)
How much does ASO Test (Antistreptolysin O) cost?
The ASO Test (Antistreptolysin O) cost is Rs.800, although it is now available for Rs.585 because of the offer.