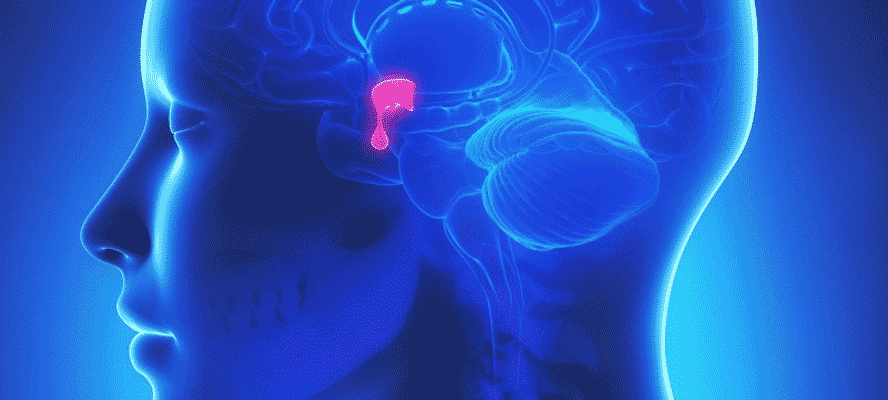
What is Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism is a rare condition that occurs when the pituitary gland fails to produce enough hormones to maintain normal bodily functions. The pituitary gland is a pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain and is responsible for secreting several hormones that control various bodily functions. When it fails to produce enough hormones, it can lead to a variety of health issues. The pituitary gland produces several hormones, including growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), and antidiuretic hormone (ADH). These hormones regulate a wide range of body functions, such as growth and development, metabolism, reproduction, and stress response.
Causes of Hypopituitarism
There are several causes of hypopituitarism, including
- Pituitary gland tumors
- Traumatic brain injury
- Brain surgery or radiation therapy
- Infections, such as meningitis or encephalitis
- Autoimmune diseases
- Genetic disorders
- Pituitary apoplexy, a sudden loss of blood supply to the pituitary gland
Importance of Identifying and Treating Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism can cause a range of health problems, including fatigue, weakness, weight gain, low blood pressure, low blood sugar, infertility, and sexual dysfunction. Left untreated, hypopituitarism can lead to more serious health problems, such as osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, and even death. Therefore, it is important to identify and treat hypopituitarism as early as possible to prevent these complications and improve quality of life.
Symptoms of Hypopituitarism
The symptoms of hypopituitarism can vary depending on which hormones are deficient. Some of the general symptoms include:
General Symptoms
- Fatigue: Fatigue is a common symptom of hypopituitarism. It can be caused by a lack of several hormones, including growth hormone, thyroid hormone, and adrenal hormone.
- Weakness: Weakness is another common symptom of hypopituitarism. It can be caused by a lack of growth hormone or adrenal hormone.
- Weight Gain: Weight gain is a common symptom of hypopituitarism. It can be caused by a lack of growth hormone or thyroid hormone, which can slow down metabolism and lead to increased fat storage.
Symptoms Specific to the Pituitary Gland
Reduced Growth Hormone (GH) Production Leading to Short Stature in Children and Adults
Growth hormone deficiency can cause short stature in children and adults. Children with growth hormone deficiency may have delayed growth and development, while adults may have decreased muscle mass and bone density.
Reduced Sex Hormone Production Leading to Sexual Dysfunction
Low levels of sex hormones, such as testosterone and estrogen, can cause sexual dysfunction in both men and women. This can include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and infertility.
Read More: Proven Way to Increase Testosterone Levels
Reduced ACTH production leading to adrenal insufficiency
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone) is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that stimulates the adrenal gland to produce cortisol. In cases of hypopituitarism, the pituitary gland may not produce enough ACTH, leading to adrenal insufficiency. This can cause symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, weight loss, low blood pressure, and electrolyte disturbance.
Reduced TSH production leading to hypothyroidism
TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) is another hormone produced by the pituitary gland that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. In cases of hypopituitarism, the pituitary gland may not produce enough TSH, leading to hypothyroidism. This can cause symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, constipation, and dry skin.
Read More: Hypothyroidism: Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and Medication
Diagnosis of Hypopituitarism
Diagnosing hypopituitarism involves a combination of physical examination, hormone level tests, imaging tests, and genetic testing.
Physical examination
During a physical examination, the doctor will look for signs and symptoms of hypopituitarism, such as decreased muscle mass, weight gain, and changes in skin tone. They will also look for signs of specific hormone deficiencies, such as delayed puberty, breast milk production in men, and changes in menstrual periods.
Hormone level tests
Hormone level tests are used to measure the levels of various hormones in the blood. The tests that may be used to diagnose hypopituitarism include:
Human Growth Hormone Test
Human Growth Hormone Test measures the levels of growth hormone in the blood. It is usually performed after the patient has fasted for several hours, and may involve several blood draws over a period of several hours.
Thyroid function tests
Thyroid Function Test measure the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood. They may include tests for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), triiodothyronine (T3), and thyroxine (T4).
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) level test
This test measures the levels of ACTH in the blood. ACTH is a hormone that stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol, a hormone that plays a role in regulating metabolism and responding to stress.
Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) level test
Luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) are two important hormones that are produced by the pituitary gland. These hormones play a crucial role in regulating the reproductive system in both men and women. A blood test can be used to measure the levels of LH and FSH in the body. Low levels of these hormones can indicate hypopituitarism, which can lead to infertility, decreased libido, and other related issues.
BOOK LUTEINISING HORMONE TEST TODAY!Imaging tests
Imaging tests are an important tool for diagnosing hypopituitarism. They can help identify any abnormalities or damage to the pituitary gland, as well as the size and location of any tumors. Two common imaging tests used for this purpose are magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scan.
BOOK WHOLE BODY CT SCAN TODAY!Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is a non-invasive imaging test that uses powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body. It is particularly useful for examining the brain and pituitary gland. During an MRI, the patient lies inside a large tube-like machine while the images are taken. The test is painless and generally takes about 30-60 minutes to complete.
Computed Tomography (CT) scan
A CT scan is another type of imaging test that uses X-rays to create detailed images of the body. During a CT scan, the patient lies on a table that moves through a large, doughnut-shaped machine. The test is painless and usually takes about 30 minutes to complete. CT scans are particularly useful for detecting abnormalities in the bones, including damage to the skull or the pituitary gland.
Genetic testing
Genetic testing is another tool that can be used to diagnose hypopituitarism. In some cases, hypopituitarism may be caused by genetic mutations or inherited disorders. Genetic testing can help identify these underlying conditions and guide treatment.
Treatment of Hypopituitarism
The treatment for hypopituitarism depends on the specific hormones that are deficient and the underlying cause of the condition. The following are some of the treatment options available for hypopituitarism.
Hormone replacement therapy
Hormone replacement therapy is the most common treatment for hypopituitarism. It involves replacing deficient hormones with synthetic hormones to restore the normal levels of hormones in the body. The following are some of the hormone replacement therapies used in the treatment of hypopituitarism.
Growth hormone replacement therapy
Growth hormone replacement therapy is used to treat growth hormone deficiency, which can cause stunted growth in children and muscle and bone loss in adults. This therapy involves daily injections of synthetic growth hormone.
Thyroid hormone replacement therapy
Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is used to treat hypothyroidism caused by a deficiency of TSH. This therapy involves taking daily doses of synthetic thyroid hormone.
Adrenal hormone replacement therapy
Adrenal hormone replacement therapy is used to treat adrenal insufficiency caused by a deficiency of ACTH. This therapy involves taking daily doses of synthetic cortisol.
Gonadal hormone replacement therapy
Gonadal hormone replacement therapy is used to treat deficiencies of sex hormones such as testosterone and estrogen. This therapy involves taking synthetic sex hormones.
Surgery
In some cases, hypopituitarism may be caused by a tumor in the pituitary gland. In such cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the tumor and restore normal hormone production. The following are some of the surgical options available for hypopituitarism.
Transsphenoidal surgery
Transsphenoidal surgery is a minimally invasive procedure in which the tumor is removed through the nose or mouth. This procedure has a high success rate and a low risk of complications.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is a treatment that uses high-energy radiation to destroy the tumor. This treatment is usually reserved for cases in which surgery is not an option or the tumor is resistant to surgery.
Medications
Hypopituitarism is usually treated with hormone replacement therapy, which involves taking medications to replace the deficient hormones. There are several medications that can be used to treat hypopituitarism, including:
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists are a type of medication that stimulates the production of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that plays a role in the production of several hormones, including prolactin. They are commonly used to treat prolactinomas, which are benign tumors of the pituitary gland that produce excessive amounts of prolactin. By reducing the production of prolactin, dopamine agonists can help improve symptoms such as menstrual irregularities, infertility, and breast milk production in women, and erectile dysfunction in men.
Somatostatin analogs
Somatostatin analogs are a type of medication that mimic the action of somatostatin, a hormone that inhibits the production of growth hormone. They are commonly used to treat acromegaly, a condition in which the pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone, leading to an overgrowth of bones and other tissues. By reducing the production of growth hormone, somatostatin analogs can help improve symptoms such as joint pain, fatigue, and enlargement of facial features and extremities.
What Makes HealthcareOnTime Your Top Choice for Diagnosing Hypopituitarism
The importance of early diagnosis and treatment cannot be overstated when it comes to hypopituitarism. If you are experiencing symptoms that may indicate hypopituitarism, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Talk to your doctor about the possibility of hypopituitarism and ask about testing options.
Hypopituitarism is a complex condition that can have a significant impact on a person’s health and well-being. With proper diagnosis and treatment, however, it is possible to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Many factors make HealthcareOnTime stand out as an outstanding option for diagnosing hypopituitarism. They provide a variety of specialist diagnostic tests that can assist in accurately detecting the underlying causes of hypopituitarism thanks to their cutting-edge laboratory capabilities.
BOOK AT HOME LAB TEST TODAY!