Subclinical Hypothyroidism Treatment: An Overview
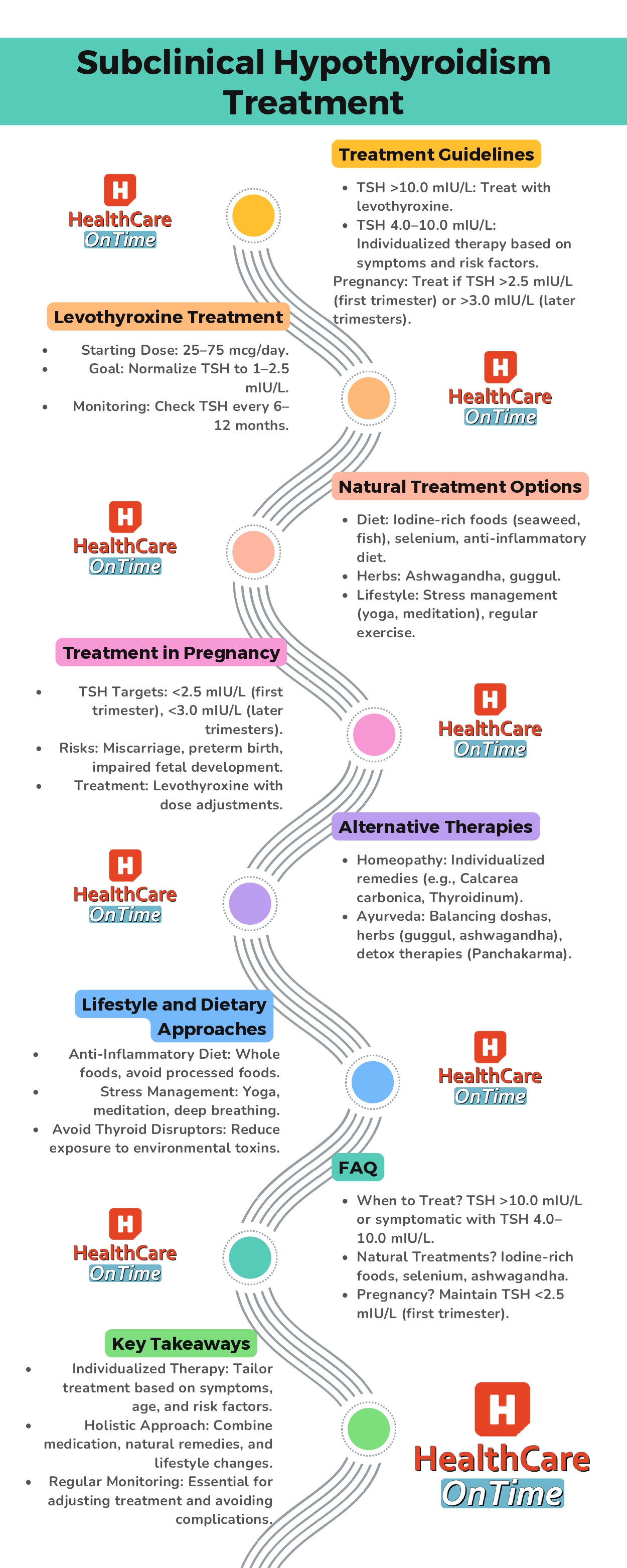
Subclinical hypothyroidism treatment focuses on managing elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels while ensuring thyroid hormone levels (T4 and T3) remain within the normal range. This condition, often detected during routine blood tests, may not always present noticeable symptoms, but it requires careful monitoring and, in some cases, intervention to prevent complications.
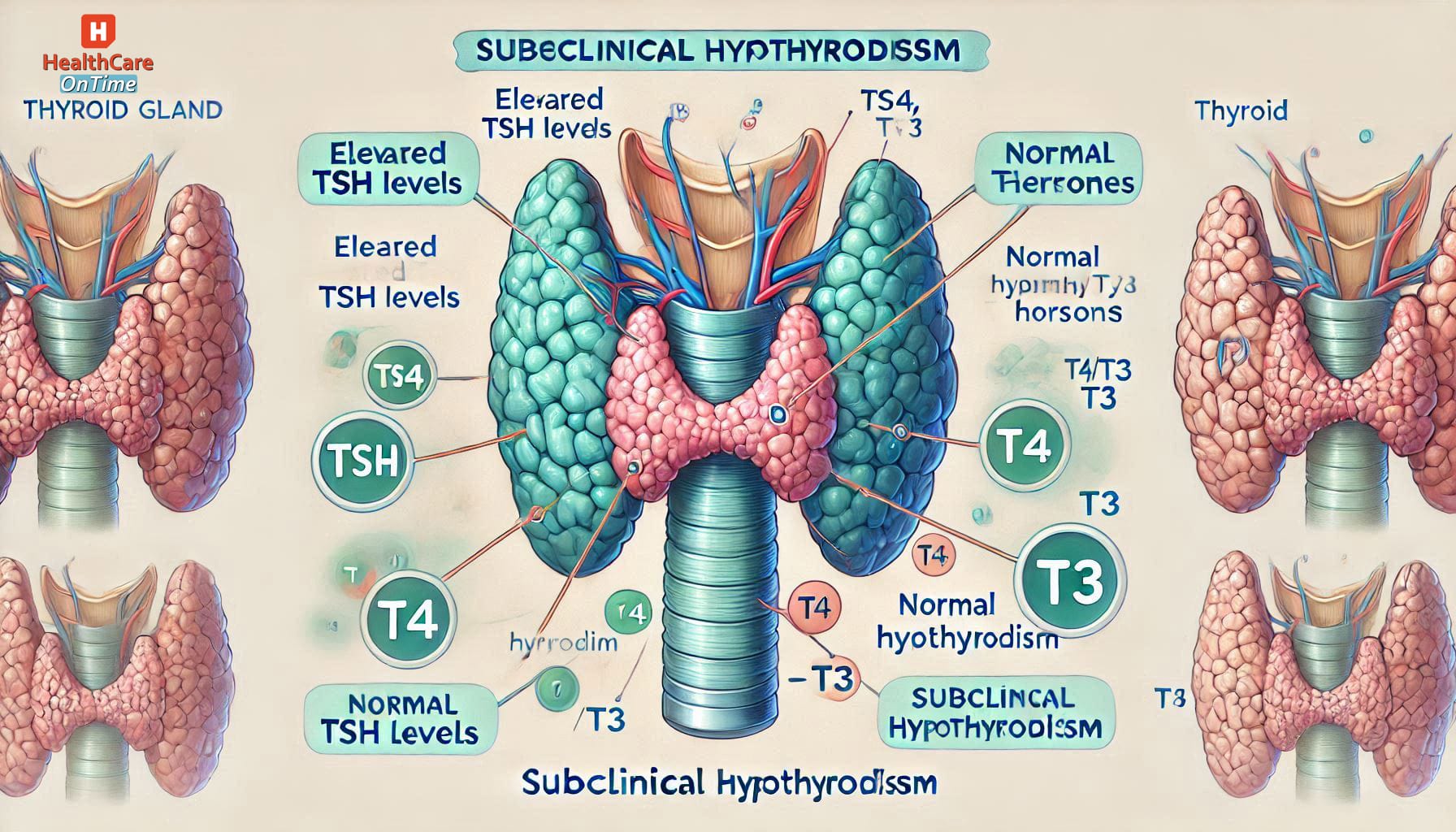
The diagnosis of SCH relies heavily on TSH levels. When TSH is elevated (typically >4.0 mIU/L) but T4 and T3 levels are normal, it indicates thyroid dysfunction. This imbalance can progress to overt hypothyroidism if left untreated, making treatment guidelines essential for effective management.
Current guidelines emphasize individualized therapy, tailoring treatment plans based on factors like age, symptoms, and the presence of comorbidities.
One of the primary goals of subclinical hypothyroidism treatment is to normalize TSH levels, often through the use of levothyroxine. The treatment dose is carefully adjusted to avoid overtreatment, which can lead to hyperthyroidism. For patients with mild SCH (TSH 4.0–10.0 mIU/L), a watchful waiting approach may be recommended, while those with elevated TSH levels above 10.0 mIU/L are typically treated more aggressively.
Untreated SCH carries significant risks, including cardiovascular disease, cognitive impairment, and mood disorders. The risk of progression to overt hypothyroidism is higher in individuals with elevated TSH levels and those who test positive for thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb). Early intervention, guided by treatment guidelines, can help mitigate these risks and improve overall health outcomes.
Subclinical hypothyroidism treatment involves a combination of monitoring, medication, and lifestyle adjustments. By addressing thyroid dysfunction and maintaining hormone balance, patients can reduce the risk of progression and enhance their quality of life.
Treatment Guidelines for Subclinical Hypothyroidism
The management of subclinical hypothyroidism treatment is guided by evidence-based treatment guidelines, which have been updated regularly to reflect the latest research. Recent guidelines from 2020 to 2023 emphasize the importance of TSH thresholds and individualized therapy to ensure optimal patient outcomes.
TSH Thresholds for Treatment
The decision to treat SCH often depends on TSH levels. For patients with TSH levels >10.0 mIU/L, treatment with levothyroxine is generally recommended to reduce the risk of progression to overt hypothyroidism and associated complications. For those with TSH levels between 4.0–10.0 mIU/L, treatment is more nuanced and depends on factors such as symptoms, age, and the presence of comorbidities like cardiovascular disease.
Levothyroxine as First-Line Treatment
Levothyroxine is the cornerstone of subclinical hypothyroidism treatment. It is a synthetic thyroid hormone that helps normalize TSH levels and restore hormone balance. The starting dose is typically low (25–75 mcg/day) and adjusted based on the patient’s response and TSH levels. Regular monitoring is essential to avoid overtreatment, which can lead to hyperthyroidism.
Monitoring and Dose Adjustments
Ongoing monitoring of TSH levels is critical in managing SCH. Patients should have their TSH levels checked every 6–12 months, with dose adjustments made as needed. Factors such as age, weight, and pregnancy status can influence the required dose, highlighting the importance of individualized therapy.
Insights from UpToDate Guidelines
The UpToDate guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations for SCH management. They stress the importance of treating patients with TSH levels >10.0 mIU/L and considering treatment for those with levels between 4.0–10.0 mIU/L if they have symptoms, cardiovascular risk factors, or positive thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb).
In summary, the latest treatment guidelines for subclinical hypothyroidism treatment emphasize the use of levothyroxine, regular monitoring of TSH levels, and individualized therapy to achieve the best outcomes. By following these guidelines, healthcare providers can effectively manage SCH and improve patients’ quality of life.
Treatment Dose for Subclinical Hypothyroidism
The treatment dose for subclinical hypothyroidism treatment is a critical factor in managing the condition effectively. The standard approach involves the use of levothyroxine, a synthetic thyroid hormone, typically starting at a low dose of 25–75 mcg/day. The goal is to achieve TSH normalization, bringing levels down to the optimal range of 1–2.5 mIU/L.
Levothyroxine Dosage and TSH Normalization
The initial levothyroxine dosage is carefully selected based on the patient’s age, weight, and overall health. For most adults, a starting dose of 25–50 mcg/day is common, with gradual increases as needed. The aim is to achieve TSH normalization without causing overtreatment, which can lead to hyperthyroidism. Regular monitoring of TSH levels is essential to ensure the dose is appropriate.
Dose Adjustments for Specific Populations
Dose adjustments are often necessary for certain groups. For example:
- Elderly patients: May require lower doses due to slower metabolism and increased sensitivity to thyroid hormone.
- Pregnant women: Often need higher doses to maintain TSH levelswithin the stricter pregnancy-specific range (e.g., <2.5 mIU/L in the first trimester).
- Patients with comorbidities: Conditions like heart disease may necessitate cautious dosing to avoid exacerbating symptoms.
Risks of Overtreatment
Overtreatment with levothyroxine can lead to hyperthyroidism, characterized by symptoms like palpitations, weight loss, and anxiety. To minimize this risk, dose adjustments should be made gradually, and TSH levels should be monitored regularly.
Treatment Indications for Specific Populations
Treatment indications vary depending on the patient’s profile. For instance:
- Elderly patients: May not require treatment unless symptoms are present or TSH levels are significantly elevated.
- Pregnant women: Treatment is often recommended even for mild SCH to prevent complications like miscarriage or preterm birth.
The treatment dose for subclinical hypothyroidism treatment is tailored to the individual, with the goal of achieving TSH normalization while avoiding overtreatment. By carefully adjusting the levothyroxine dosage and considering factors like age and pregnancy status, healthcare providers can optimize outcomes for their patients.
Treatment Without Medication: Lifestyle and Dietary Approaches
For individuals with subclinical hypothyroidism treatment, lifestyle and dietary approaches can play a significant role in managing the condition, especially for those who prefer treatment without medication. These strategies focus on improving overall health, reducing inflammation, and supporting thyroid function naturally.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet
An anti-inflammatory diet is one of the most effective ways to support thyroid health. This involves:
- Eating whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Avoiding processed foods, refined sugars, and trans fats, which can exacerbate inflammation.
- Incorporating iodine-rich foods like seaweed, fish, and iodized salt to support thyroid hormone production.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can negatively impact thyroid function. Practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress levels and improve overall well-being. These techniques not only reduce cortisol levels but also support hormone balance.
Regular Exercise and Sleep Hygiene
Engaging in regular exercise can boost metabolism and improve energy levels, which are often affected by SCH. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity, such as walking or swimming, most days of the week. Additionally, prioritizing sleep hygiene—such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a restful environment—can help regulate hormone production and improve overall health.
Avoiding Thyroid Disruptors
Environmental toxins, known as thyroid disruptors, can interfere with thyroid function. To minimize exposure:
- Use glass or stainless steel containers instead of plastic.
- Choose organic produce to reduce pesticide exposure.
- Filter drinking water to remove contaminants like fluoride and chlorine.
Lifestyle and dietary approaches offer a natural way to manage subclinical hypothyroidism treatment. By adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, practicing stress management, exercising regularly, and avoiding thyroid disruptors, individuals can support their thyroid health and improve their quality of life without relying solely on medication.
Mild Subclinical Hypothyroidism Treatment
For individuals with mild subclinical hypothyroidism treatment, a watchful waiting approach is often recommended, especially when TSH levels are between 4.0–10.0 mIU/L and symptoms are minimal or absent. This strategy focuses on monitoring and lifestyle changes rather than immediate medication.
Watchful Waiting Approach
The watchful waiting approach involves regular monitoring of TSH levels through periodic blood tests. This allows healthcare providers to track any changes and intervene only if necessary. For many patients, especially those with mild SCH, this approach avoids unnecessary medication and its potential side effects.
Symptom Management and Lifestyle Interventions
Even in mild cases, symptom management can improve quality of life. Common symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, and brain fog can often be addressed through lifestyle interventions, such as:
- Adopting an anti-inflammatory dietrich in whole foods.
- Engaging in regular exerciseto boost energy and metabolism.
- Practicing stress managementtechniques like yoga or meditation.
Periodic Monitoring of TSH Levels
Periodic monitoring is a cornerstone of managing mild SCH. Patients should have their TSH levels checked every 6–12 months to detect any progression. If TSH levels rise above 10.0 mIU/L or symptoms worsen, treatment with levothyroxine may be considered.
Risks of Progression to Overt Hypothyroidism
While mild SCH often remains stable, there is a risk of progression to overt hypothyroidism, especially in individuals with elevated thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb). Regular monitoring helps identify this progression early, allowing for timely intervention.
Natural Treatments for Mild SCH
For those preferring treatment without medication, natural treatments can be beneficial. These include:
- Selenium supplementationto support thyroid function.
- Ashwagandha, an adaptogen that may help balance thyroid hormones.
- Probioticsto improve gut health, which plays a role in thyroid hormone conversion.
Mild subclinical hypothyroidism treatment often involves a watchful waiting approach, supported by symptom management and lifestyle interventions. By focusing on periodic monitoring and incorporating natural treatments, patients can effectively manage their condition and reduce the risk of progression to overt hypothyroidism.
Natural Treatment for Subclinical Hypothyroidism
For individuals seeking alternatives to medication, natural treatment options can be highly effective in managing subclinical hypothyroidism treatment. These approaches focus on supporting thyroid function through lifestyle and dietary approaches, reducing inflammation, and addressing underlying imbalances.
Iodine-Rich Foods
Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone production, and incorporating iodine-rich foods into the diet can help. Examples include:
- Seaweed: A potent source of iodine, but should be consumed in moderation to avoid excess.
- Fish: Especially cod, tuna, and shrimp, which provide both iodine and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Iodized salt: A simple way to ensure adequate iodine intake.
Selenium Supplementation
Selenium is a trace mineral that plays a crucial role in thyroid health. It helps convert T4 (inactive thyroid hormone) into T3 (active thyroid hormone) and protects the thyroid gland from oxidative damage. Brazil nuts, sunflower seeds, and supplements are excellent sources of selenium.
Ashwagandha for Thyroid Support
Ashwagandha, an adaptogenic herb, has been shown to support thyroid function by balancing hormone levels and reducing stress. Studies suggest it may help improve TSH, T4, and T3 levels in individuals with mild SCH.
Probiotics and Gut Health
The gut-thyroid connection is well-established, and maintaining a healthy gut is vital for thyroid function. Probiotics can help restore gut flora, improve digestion, and enhance the conversion of thyroid hormones. Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut are excellent natural sources.
Anti-Inflammatory Herbs
Chronic inflammation can worsen thyroid dysfunction. Incorporating anti-inflammatory herbs like turmeric and ginger into the diet can help reduce inflammation and support overall thyroid health. These herbs can be consumed as teas, supplements, or added to meals.
Natural treatment for subclinical hypothyroidism treatment offers a holistic approach to managing the condition. By focusing on iodine-rich foods, selenium supplementation, ashwagandha, probiotics, and anti-inflammatory herbs, individuals can support their thyroid health naturally and improve their quality of life.
Treatment in Pregnancy: Special Considerations
Treatment in pregnancy for subclinical hypothyroidism treatment is critical to ensure the health of both the mother and the developing baby. SCH during pregnancy can lead to complications if left untreated, making it essential to follow treatment guidelines and monitor thyroid function closely.
TSH Thresholds in Pregnancy
Pregnant women have stricter TSH thresholds compared to the general population. For example:
- First trimester: TSH should be below 5 mIU/L.
- Second and third trimesters: TSH should be below 0 mIU/L.These stricter thresholds are necessary because even mild thyroid dysfunction can impact fetal development and pregnancy outcomes.
Risks of Untreated SCH in Pregnancy
Untreated SCH during pregnancy carries significant risks, including:
- Miscarriage: Elevated TSH levels are associated with a higher risk of pregnancy loss.
- Preterm birth: SCH can increase the likelihood of delivering before 37 weeks.
- Impaired fetal brain development: Thyroid hormones are crucial for the baby’s brain development, particularly in the first trimester.
Levothyroxine and Dose Adjustments
Levothyroxine is the standard treatment for SCH during pregnancy. The levothyroxine dosage often needs to be adjusted to maintain optimal TSH levels. For example:
- Pregnant women may require a 20–30% increasein their levothyroxine dose, especially during the first trimester.
- Regular monitoring of TSH levels is essential to ensure the dose is appropriate and to make adjustments as needed.
Insights from Treatment Guidelines
According to treatment guidelines, pregnant women with SCH should:
- Begin treatment if TSH levels exceed 5 mIU/Lin the first trimester or 3.0 mIU/L in later trimesters.
- Be monitored every 4–6 weeks to ensure TSH levels remain within the target range.
- Continue treatment postpartum if TSH levels remain elevated.
Treatment in pregnancy for subclinical hypothyroidism treatment is vital to prevent complications like miscarriage and preterm birth. By adhering to TSH thresholds in pregnancy, using levothyroxine, and following treatment guidelines, healthcare providers can ensure a healthy pregnancy and optimal outcomes for both mother and baby.
Treatment Indications for Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Determining the treatment indications for subclinical hypothyroidism treatment involves evaluating symptoms, risk factors, and specific patient populations. While not all cases of SCH require immediate treatment, certain factors make intervention necessary to prevent complications.
Symptoms and Risk Factors
The decision to treat SCH often depends on the presence of symptoms and underlying risk factors. Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, and cognitive issues, which can significantly impact quality of life. Additionally, risk factors such as cardiovascular disease and cognitive impairment may warrant treatment, even in the absence of severe symptoms.
Role of Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies (TPOAb)
The presence of thyroid peroxidase antibodies (TPOAb) is a key indicator of autoimmune thyroid disease, such as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Patients with elevated TPOAb levels are at a higher risk of progressing to overt hypothyroidism, making treatment more likely. Studies show that TPOAb-positive individuals benefit from early intervention to prevent long-term complications.
Individualized Therapy for Elderly Patients
Elderly patients often require individualized therapy due to their unique health profiles. For example, older adults may have comorbidities like heart disease or osteoporosis, which can influence treatment decisions. In some cases, a watchful waiting approach is preferred to avoid overtreatment and its associated risks, such as atrial fibrillation.
Risks of Cardiovascular Disease and Cognitive Impairment
Untreated SCH is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including hypertension and atherosclerosis. Additionally, cognitive impairment and mood disorders are more common in individuals with elevated TSH levels. These risks highlight the importance of timely treatment, especially in symptomatic patients.
Treatment Guidelines for Specific Populations
Treatment guidelines recommend considering treatment for:
- Patients with TSH levels >10.0 mIU/L, regardless of symptoms.
- Symptomatic individuals with TSH levels between 4.0–10.0 mIU/L.
- Pregnant women or those planning pregnancy with TSH levels >2.5 mIU/L.
- TPOAb-positiveindividuals with elevated TSH levels.
In summary, treatment indications for subclinical hypothyroidism treatment are based on a combination of symptoms, risk factors, and patient-specific considerations. By following treatment guidelines and adopting an individualized therapy approach, healthcare providers can effectively manage SCH and reduce the risks of cardiovascular disease and cognitive impairment.
Homeopathy Treatment for Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Homeopathy treatment is an alternative approach to managing subclinical hypothyroidism treatment, focusing on individualized remedies and addressing the root causes of thyroid dysfunction. While it is often considered a natural treatment option, it is important to understand its limitations and consult a qualified homeopath for personalized care.
Individualized Remedies
Homeopathy is based on the principle of treating the individual as a whole, rather than just the symptoms. A qualified homeopath will assess the patient’s physical, emotional, and mental health to prescribe individualized remedies. For example:
- Calcarea carbonica: Often recommended for fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold.
- Thyroidinum: Used to support thyroid function and balance hormone levels.
- Nux vomica: May be prescribed for stress-related thyroid issues.
Lack of Strong Evidence
While some patients report improvements with homeopathy treatment, there is a lack of strong evidence to support its effectiveness for SCH. Clinical studies on homeopathy for thyroid conditions are limited, and more research is needed to validate its benefits.
Consulting a Qualified Homeopath
If considering homeopathy treatment, it is crucial to consult a qualified homeopath who can tailor remedies to your specific needs. Self-prescribing or relying on unverified sources can lead to ineffective or unsafe treatment.
Homeopathic Remedies for Thyroid Health
Some commonly used homeopathic remedies for thyroid health include:
- Iodum: For individuals with rapid metabolism and weight loss.
- Lycopodium: For those experiencing bloating and digestive issues alongside thyroid problems.
- Sepia: Often recommended for hormonal imbalances and fatigue.
Homeopathy treatment offers a holistic approach to subclinical hypothyroidism treatment, focusing on individualized remedies and addressing root causes. However, due to the lack of strong evidence, it should be used cautiously and under the guidance of a qualified homeopath.
Ayurveda Treatment for Subclinical Hypothyroidism
Ayurveda treatment offers a holistic approach to managing subclinical hypothyroidism treatment, focusing on restoring balance to the body and mind. Rooted in ancient Indian medicine, Ayurveda emphasizes the importance of balancing doshas (Vata, Pitta, Kapha) and using natural treatments to support thyroid health.
Balancing Doshas
According to Ayurveda, thyroid dysfunction is often linked to an imbalance in the doshas, particularly Kapha and Vata. To restore balance, Ayurvedic practitioners recommend:
- Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, yoga, and meditation to reduce stress and improve energy flow.
- Herbal remedies: Using herbs like gugguland ashwagandha to support thyroid function and hormone balance.
Benefits of Herbs
- Guggul: Known for its anti-inflammatory properties, guggul helps stimulate thyroid activity and improve metabolism.
- Ashwagandha: An adaptogen that supports hormone regulation and reduces stress, which can indirectly benefit thyroid health.
Dietary Recommendations
Ayurveda emphasizes the importance of diet in managing SCH. Key recommendations include:
- Eating warm, cooked foodsthat are easy to digest, such as soups, stews, and steamed vegetables.
- Avoiding cold, raw, and processed foods, which can aggravate Kaphaand slow metabolism.
- Incorporating iodine-rich foods like seaweed and iodized salt to support thyroid function.
Detoxification Therapies
Ayurveda also recommends detoxification therapies like Panchakarma to cleanse the body and restore balance. Panchakarma involves a series of treatments, including massages, herbal steam therapy, and dietary changes, to eliminate toxins and improve overall health.
Ayurveda treatment provides a comprehensive approach to subclinical hypothyroidism treatment, focusing on balancing doshas, using natural treatments like guggul and ashwagandha, and following dietary recommendations. By incorporating these practices, individuals can support their thyroid health and improve their overall well-being.
In summary, subclinical hypothyroidism treatment requires a personalized approach, combining individualized therapy with lifestyle changes to achieve optimal outcomes. While conventional treatments like levothyroxine are effective, natural treatments, homeopathy, and Ayurveda offer holistic alternatives for those seeking complementary care. Always consult a healthcare provider to create a tailored treatment plan that addresses your unique needs and ensures the best results.